Page 44 - Chip Scale Review_January-February_2024-digital
P. 44
Results and discussion
The sections below discuss the precise
bond energy measurement done by DCB
and by NI.
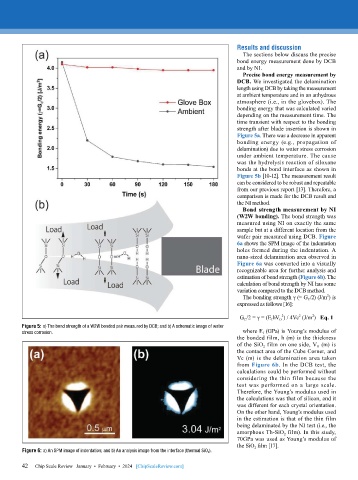
Precise bond energy measurement by
DCB. We investigated the delamination
length using DCB by taking the measurement
at ambient temperature and in an anhydrous
atmosphere (i.e., in the glovebox). The
bonding energy that was calculated varied
depending on the measurement time. The
time transient with respect to the bonding
strength after blade insertion is shown in
Figure 5a. There was a decrease in apparent
bonding energy (e.g., propagation of
delamination) due to water stress corrosion
under ambient temperature. The cause
was the hydrolysis reaction of siloxane
bonds at the bond interface as shown in
Figure 5b [10-12]. The measurement result
can be considered to be robust and repeatable
from our previous report [13]. Therefore, a
comparison is made for the DCB result and
the NI method.
Bond strength measurement by NI
(W2W bonding). The bond strength was
measured using NI on exactly the same
sample but at a different location from the
wafer pair measured using DCB. Figure
6a shows the SPM image of the indentation
holes formed during the indentation. A
nano-sized delamination area observed in
Figure 6a was converted into a visually
recognizable area for further analysis and
estimation of bond strength (Figure 6b). The
calculation of bond strength by NI has some
variation compared to the DCB method.
The bonding strength γ (= G C /2) (J/m ) is
2
expressed as follows [16]:
G C /2 = γ = (E f hV O ) / 4Vc (J/m ) Eq. 1
2
2
2
Figure 5: a) The bond strength of a W2W bonded pair measured by DCB; and b) A schematic image of water
stress corrosion. where E f (GPa) is Young’s modulus of
the bonded film, h (m) is the thickness
of the SiO 2 film on one side, V O (m) is
the contact area of the Cube Corner, and
Vc (m) is the delamination area taken
from Figure 6b. In the DCB test, the
calculations could be performed without
considering the thin film because the
test was performed on a large scale.
Therefore, the Young’s modulus used in
the calculations was that of silicon, and it
was different for each crystal orientation.
On the other hand, Young’s modulus used
in the estimation is that of the thin film
being delaminated by the NI test (i.e., the
amorphous Th-SiO 2 film). In this study,
70GPa was used as Young’s modulus of
the SiO 2 film [17].
Figure 6: a) An SPM image of indentation; and b) An analysis image from the interface (thermal SiO 2 ).
42
42 Chip Scale Review January • February • 2024 [ChipScaleReview.com]