Page 23 - Chip Scale Review_March April_2023-digital
P. 23
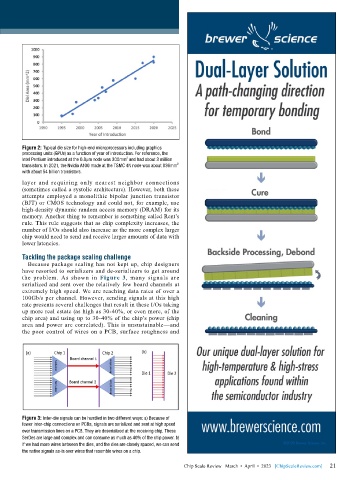
Figure 2: Typical die size for high-end microprocessors including graphics
processing units (GPUs) as a function of year of introduction. For reference, the
2
Intel Pentium introduced at the 0.8μm node was 300mm and had about 3 million
transistors. In 2021, the Nvidia A100 made at the TSMC 4N node was about 836mm 2
with about 54 billion transistors.
layer and requiring only nearest neighbor connections
(sometimes called a systolic architecture). However, both these
attempts employed a monolithic bipolar junction transistor
(BJT) or CMOS technology and could not, for example, use
high-density dynamic random access memory (DRAM) for its
memory. Another thing to remember is something called Rent’s
rule. This rule suggests that as chip complexity increases, the
number of I/Os should also increase as the more complex larger
chip would need to send and receive larger amounts of data with
lower latencies.
Tackling the package scaling challenge
Because package scaling has not kept up, chip designers
have resorted to serializers and de-serializers to get around
the problem. As shown in Figure 3, many signals are
serialized and sent over the relatively few board channels at
extremely high speed. We are reaching data rates of over a
100Gb/s per channel. However, sending signals at this high
rate presents several challenges that result in these I/Os taking
up more real estate (as high as 30-40%, or even more, of the
chip area) and using up to 30-40% of the chip’s power (chip
area and power are correlated). This is unsustainable—and
the poor control of wires on a PCB, surface roughness and
Figure 3: Inter-die signals can be handled in two different ways: a) Because of
fewer inter-chip connections on PCBs, signals are serialized and sent at high speed
over transmission lines on a PCB. They are deserialized at the receiving chip. These
SerDes are large and complex and can consume as much as 40% of the chip power. b)
If we had more wires between the dies, and the dies are closely spaced, we can send
the native signals as-is over wires that resemble wires on a chip.
21
Chip Scale Review March • April • 2023 [ChipScaleReview.com] 21