Page 25 - Chip Scale Review_March April_2023-digital
P. 25
2
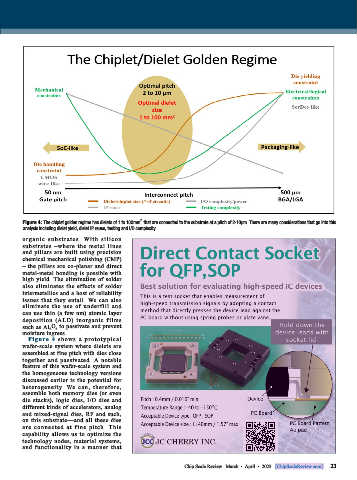
Figure 4: The chiplet golden regime has dielets of 1 to 100mm that are connected to the substrate at a pitch of 2-10μm. There are many considerations that go into this
analysis including dielet yield, dielet IP reuse, testing and I/O complexity.
organ ic subst rates. With silicon
substrates –where the metal lines
and pillars are built using precision
chemical mechanical polishing (CMP)
– the pillars are co-planar and direct
metal-metal bonding is possible with
high yield. The elimination of solder
also eliminates the effects of solder
intermetallics and a host of reliability
issues that they entail. We can also
eliminate the use of underfill and
can use thin (a few nm) atomic layer
deposition (ALD) inorganic films
such as Al 2 O 3 to passivate and prevent
moisture ingress.
Figure 4 shows a protot y pical
wafer-scale system where dielets are
assembled at fine pitch with dies close
together and passivated. A notable
feature of this wafer-scale system and
the homogeneous technology versions
discussed earlier is the potential for
heterogeneity. We can, therefore,
assemble both memory dies (or even
die stacks), logic dies, I/O dies and
different kinds of accelerators, analog
and mixed-signal dies, RF and such,
on this substrate—and all these dies
are connected at f ine pitch. This
capability allows us to optimize the
technology nodes, material systems,
and functionality in a manner that
23
Chip Scale Review March • April • 2023 [ChipScaleReview.com] 23