Page 20 - ChipScale_Mar-Apr_2020-digital
P. 20
The die placement and spacing on the Both no UBM and UBM options were mechanical dicing to fragile BEOL layers
metal carrier was determined by the evaluated. SACA and SACB were the leads to their delamination and cracking.
final FOWLP design. After die pick and two lead-free solder alloys used. Diel 1 Laser groove was performed first to separate
place, the wafer was molded and the and Diel 2 are two different repassivation the BEOL layers, followed by mechanical
carrier wafer was removed. This step is (REP) dielectric materials. In conjunction blade dicing. The scribe lines had varying
followed by a package RDL fabrication with the different solder alloys, appropriate metal densities in different locations, so
process with five or six lithography package interconnect stack-ups were a laser groove recipe was developed over
layers to form either the under bump evaluated to optimize reliability stresses a series of DOE to optimize the process
metallization (UBM), or no UBM design across different levels of interconnects parameters that achieve all the following
version, respectively. ranging from silicon BEOL, package objectives: 1) no peeling/delamination of
After RDL formation, the mold wafer RDLs and package, and PCB solder joint. LK/ELK BEOL; 2) removing all metal from
was background to the final package Figures 4 and 5 show scribe line high-density metal locations (to eliminate
thickness, followed by solder ball drop and structures from the front (active) and back the potential for metal debris in the scribe
package singulation into individual units. sides of the silicon wafer from high-metal line); and 3) optimum laser groove depth.
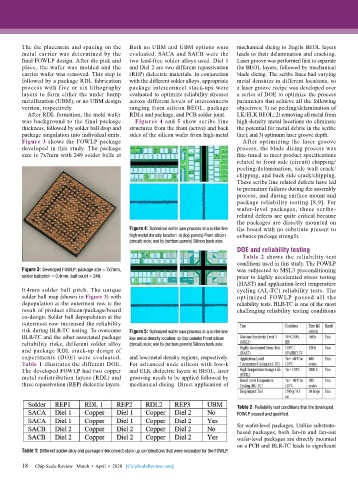
Figure 3 shows the FOWLP package After optimizing the laser groove
developed in this study. The package process, the blade dicing process was
size is 7x7mm with 249 solder balls at fine-tuned to meet product specifications
related to front side (circuit) chipping/
peeling/delamination, side wall crack/
chipping, and back side crack/chipping.
These scribe line related defects have led
to premature failures during the assembly
process, and during surface mount and
package reliability testing [8,9]. For
wafer-level packages, these scribe-
related defects are quite critical because
the packages are directly mounted on
Figure 4: Optimized wafer saw process at a scribe line the board with no substrate present to
high metal density location: a) (top panels) Front silicon enhance package strength.
(circuit) side; and b) (bottom panels) Silicon back side.
DOE and reliability testing
Table 2 shows the reliability test
conditions used in this study. The FOWLP
Figure 3: Developed FOWLP: package size = 7x7mm, was subjected to MSL3 preconditioning
solder ball pitch = 0.4mm, ball count = 249. prior to highly accelerated stress testing
(HAST) and application-level temperature
0.4mm solder ball pitch. The unique cycling (AL-TC) reliability tests. The
solder ball map (shown in Figure 3) with optimized FOWLP passed all the
depopulation at the outermost row is the reliability tests. BLR-TC is one of the most
result of product silicon/package/board challenging reliability testing conditions
co-design. Solder ball depopulation at the
outermost row increased the reliability
risk during BLR-TC testing. To overcome Figure 5: Optimized wafer saw process at a scribe line
BLR-TC and the other associated package low metal density location: a) (top panels) Front silicon
reliability risks, different solder alloy (circuit) side; and b) (bottom panels) Silicon back side.
and package RDL stack-up design of
experiments (DOE) were evaluated. and low-metal density regions, respectively.
Table 1 illustrates the different DOE. For advanced node silicon with low-k
The developed FOWLP had two copper and ELK dielectric layers in BEOL, laser
metal redistribution layers (RDL) and grooving needs to be applied followed by
three repassivation (REP) dielectric layers. mechanical dicing. Direct application of
Table 2: Reliability test conditions that the developed
FOWLP passed and qualified.
for wafer-level packages. Unlike substrate-
based packages, both fan-in and fan-out
wafer-level packages are directly mounted
on a PCB and BLR-TC leads to significant
Table 1: Different solder alloy and package interconnect stack up combinations that were evaluated for the FOWLP.
18
18 Chip Scale Review March • April • 2020 [ChipScaleReview.com]