Page 23 - ChipScale_May-June_2020-digital
P. 23
OTA far-field testing
OTA far-field testing on ATE usually
means that although the measurement
antenna is on the far-field, neither the
AiP DUT, nor the measurement antenna
move—they stay static at a certain
predefined distance. This means that no
traditional beam forming measurements
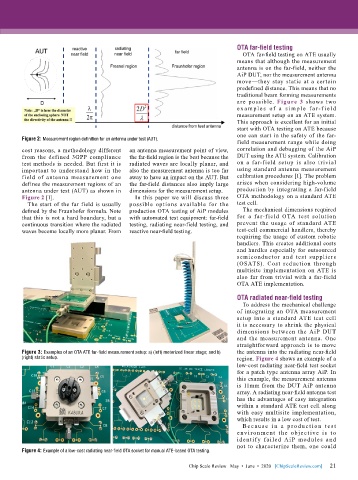
are possible. Figure 3 shows two
e x a m p l e s of a s i m p l e f a r-f i e l d
measurement setup on an ATE system.
This approach is excellent for an initial
start with OTA testing on ATE because
one can start in the safety of the far-
Figure 2: Measurement region definition for an antenna under test (AUT).
field measurement range while doing
cost reasons, a methodology different an antenna measurement point of view, correlation and debugging of the AiP
from the defined 3GPP compliance the far-field region is the best because the DUT using the ATE system. Calibration
test methods is needed. But first it is radiated waves are locally planar, and on a far-field setup is also trivial
important to understand how in the also the measurement antenna is too far using standard antenna measurement
field of antenna measurement one away to have an impact on the AUT. But calibration procedures [1]. The problem
defines the measurement regions of an the far-field distances also imply large arises when considering high-volume
antenna under test (AUT) as shown in dimensions for the measurement setup. production by integrating a far-field
Figure 2 [1]. In this paper we will discuss three OTA methodology on a standard ATE
The start of the far field is usually possible options available for the test cell.
defined by the Fraunhofer formula. Note production OTA testing of AiP modules The mechanical dimensions required
that this is not a hard boundary, but a with automated test equipment: far-field for a far-f ield OTA test solution
continuous transition where the radiated testing, radiating near-field testing, and prevent the usage of standard ATE
waves become locally more planar. From reactive near-field testing. test-cell commercial handlers, thereby
requiring the usage of custom robotic
handlers. This creates additional costs
and hurdles especially for outsourced
semiconductor and test suppliers
(OSATS). Cost reduction through
multisite implementation on ATE is
also far from trivial with a far-field
OTA ATE implementation.
OTA radiated near-field testing
To address the mechanical challenge
of integrating an OTA measurement
setup into a standard ATE test cell
it is necessary to shrink the physical
dimensions between the AiP DUT
and the measurement antenna. One
straightforward approach is to move
Figure 3: Examples of an OTA ATE far-field measurement setup: a) (left) motorized linear stage; and b) the antenna into the radiating near-field
(right) static setup. region. Figure 4 shows an example of a
low-cost radiating near-field test socket
for a patch type antenna array AiP. In
this example, the measurement antenna
is 11mm from the DUT AiP antenna
array. A radiating near-field antenna test
has the advantages of easy integration
within a standard ATE test cell along
with easy multisite implementation,
which results in a low cost of test.
B e c a u s e i n a p r o d u c t io n t e s t
e nv i ron me nt t he obje ct ive is t o
identif y failed AiP modules and
not to characterize them, one could
Figure 4: Example of a low-cost radiating near-field OTA socket for manual ATE-based OTA testing.
21
Chip Scale Review May • June • 2020 [ChipScaleReview.com] 21