Page 13 - Chip Scale Review_November-December_2023-digital
P. 13
Die placement accuracy
Two bonding process cornerstones
include bond force control and bond front
propagation, of which the latter can be
controlled through several options—with
die shaping being preferred. The die shaping
is responsible for creating a controlled
bond front, ensuring no void entrapment,
and avoiding ablation generated from the
high-speed die bond to substrate wafer.
Bond force, in turn, can impact initial bond
strength from dielectric fusion as well as
damage to the die if force is not controlled
or not optimized.
Our approach to die shaping and bond
front propagation is to have a single point
of initial contact between die and substrate
wafer, which is at the center of the die. This
approach ensures two things: first, the initial
contact causes instant bonding through Van
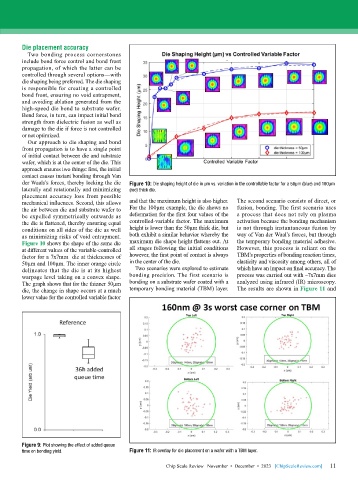
der Waals’s forces, thereby locking the die Figure 10: Die shaping height of die in µm vs. variation in the controllable factor for a 50µm (blue) and 100µm
laterally and rotationally and minimizing (red) thick die.
placement accuracy loss from possible
mechanical influences. Second, this allows and that the maximum height is also higher. The second scenario consists of direct, or
the air between die and substrate wafer to For the 100µm example, the die shows no fusion, bonding. The first scenario uses
be expelled symmetrically outwards as deformation for the first four values of the a process that does not rely on plasma
the die is flattened, thereby ensuring equal controlled-variable factor. The maximum activation because the bonding mechanism
conditions on all sides of the die as well height is lower than the 50µm thick die, but is not through instantaneous fusion by
as minimizing risks of void entrapment. both exhibit a similar behavior whereby the way of Van der Waal’s forces, but through
Figure 10 shows the shape of the same die maximum die shape height flattens out. At the temporary bonding material adhesive.
at different values of the variable-controlled all stages following the initial conditions However, this process is reliant on the
factor for a 7x7mm die at thicknesses of however, the first point of contact is always TBM’s properties of bonding reaction times,
50µm and 100µm. The inner orange circle in the center of the die. elasticity and viscosity among others, all of
delineates that the die is at its highest Two scenarios were explored to estimate which have an impact on final accuracy. The
warpage level taking on a convex shape. bonding precision. The first scenario is process was carried out with ~7x7mm dies
The graph shows that for the thinner 50µm bonding on a substrate wafer coated with a analyzed using infrared (IR) microscopy.
die, the change in shape occurs at a much temporary bonding material (TBM) layer. The results are shown in Figure 11 and
lower value for the controlled variable factor
Figure 9: Plot showing the effect of added queue
time on bonding yield. Figure 11: IR overlay for die placement on a wafer with a TBM layer.
Chip Scale Review November • December • 2023 [ChipScaleReview.com] 11 11