Page 52 - ChipScale_Mar-Apr_2020-digital
P. 52
Table 4: QTC data for MR and LAB DOE.
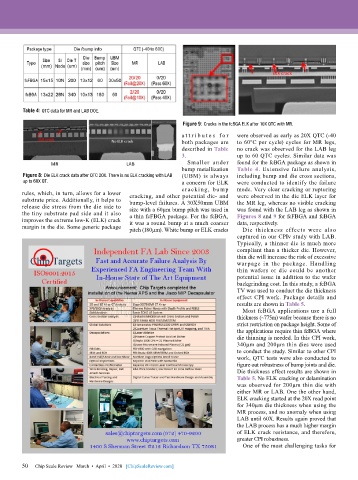
Figure 9: Cracks in the fcBGA ELK after 10X QTC with MR.
a t t r i bu t e s f o r were observed as early as 20X QTC (-40
both packages are to 60ºC per cycle) cycles for MR legs,
described in Table no crack was observed for the LAB leg
3. up to 60 QTC cycles. Similar data was
Smaller under found for the fcBGA package as shown in
bump metallization Table 4. Extensive failure analysis,
Figure 8: Die ELK crack data after QTC 20X. There is no ELK cracking with LAB (UBM) is always including bump and die cross sections,
up to 60X QT. a concern for ELK were conducted to identify the failure
crack ing, bu mp mode. Very clear cracking or rupturing
rules, which, in turn, allows for a lower cracking, and other potential die- and were observed in the die ELK layer for
substrate price. Additionally, it helps to bump-level failures. A 30X50mm UBM the MR leg, whereas no visible cracking
release die stress from the die side to size with a 60µm bump pitch was used in was found with the LAB leg as shown in
the tiny substrate pad side and it also a thin fcFBGA package. For the fcBGA, Figures 8 and 9 for fcFBGA and fcBGA
improves the extreme low-K (ELK) crack it was a round bump at a much coarser data, respectively.
margin in the die. Some generic package pitch (180µm). White bump or ELK cracks Die thickness effects were also
captured in our CPIv study with LAB.
Typically, a thinner die is much more
compliant than a thicker die. However,
thin die will increase the risk of excessive
warpage in the package. Handling
thin wafers or die could be another
potential issue in addition to the wafer
backgrinding cost. In this study, a fcBGA
TV was used to conduct the die thickness
effect CPI work. Package details and
results are shown in Table 5.
Most fcBGA applications use a full
thickness (~775m) wafer because there is no
strict restriction on package height. Some of
the applications require thin fcBGA where
die thinning is needed. In this CPI work,
340µm and 200µm thin dies were used
to conduct the study. Similar to other CPI
work, QTC tests were also conducted to
figure out robustness of bump joints and die.
Die thickness effect results are shown in
Table 5. No ELK cracking or delamination
was observed for 200µm thin die with
either MR or LAB. One the other hand,
ELK cracking started at the 20X read point
for 340µm die thickness when using the
MR process, and no anomaly when using
LAB until 60X. Results again proved that
the LAB process has a much higher margin
of ELK crack resistance, and therefore,
greater CPI robustness.
One of the most challenging tasks for
50
50 Chip Scale Review March • April • 2020 [ChipScaleReview.com]