Page 36 - ChipScale_Mar-Apr_2020-digital
P. 36
in development. The next generation of
bonders will push bonding pitch to the
ultra-fine region where revolutionary 3D-
IC integration can be enabled.
Fine-pitch example
Future HBM and DRAM packaging
is expected to scale below 40µm. Our
new bonding method can enable at
least two generations of pitch scaling
and the alignment accuracy can be met
with existing high-precision flip-chip
bonders. The two challenges addressed
in our development are low-temperature
anneal and multi-layer stacking. We have
demonstrated solid Cu-to-Cu joints after a
200ºC/1 hour anneal with very high yield,
as shown in Table 2 and Figure 6 [9].
This proof point of low thermal budget
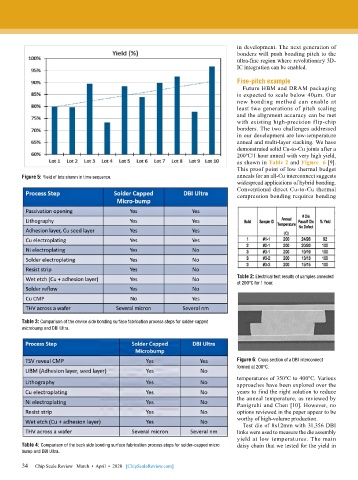
Figure 5: Yield of lots shown in time sequence. anneals for an all-Cu interconnect suggests
widespread applications of hybrid bonding.
Conventional direct Cu-to-Cu thermal
compression bonding requires bonding
Table 2: Electrical test results of samples annealed
at 200ºC for 1 hour.
Table 3: Comparison of the device side bonding surface fabrication process steps for solder-capped
microbump and DBI Ultra.
Figure 6: Cross section of a DBI interconnect
formed at 200ºC.
temperatures of 350ºC to 400ºC. Various
approaches have been explored over the
years to find the right solution to reduce
the anneal temperature, as reviewed by
Panigrahi and Chen [10]. However, no
options reviewed in the paper appear to be
worthy of high-volume production.
Test die of 8x12mm with 31,356 DBI
links were used to measure the die assembly
yield at low temperatures. The main
Table 4: Comparison of the back side bonding surface fabrication process steps for solder-capped micro daisy chain that we tested for the yield in
bump and DBI Ultra.
34 Chip Scale Review March • April • 2020 [ChipScaleReview.com]
34