Page 45 - Chip Scale Review_May June_2022-digital
P. 45
Fan-in wafer-level packaging: any chip can be a flip chip!
By Ray Fillion [Fillion Consulting]
I n the November/December issue smaller footprint, thinner devices directly on a semiconductor wafer, and
of Chip Scale Review, seven
advanced packaging technologies for thinner, lighter products with 2) molded-wafer RDL processing, which
increased functionality. Without fan-
is processing on a reconstituted, molded
were described [1]. The article covered in technologies, personal electronic wafer. Both of these FIWLP approaches
embedded chip packaging (ECP), fan-in products could not be as thin, as light utilize 300mm semiconductor wafer
wafer-level packaging (FIWLP), fan-out and as small as they are, and still have processing equipment.
wafer-level and panel-level packaging the functionality and performance that On-wafer FIWLP devices. A typical
(FOWLP, FOPLP), 3D chip stacking, they have. on-wafer FIWLP device is depicted
package-on-package (PoP) stacking and As indicated by their name, fan- in perspective view (top) and cross-
system-in-package (SiP) and compared in devices reconfigure I/O pads from sectional view (bottom) in Figure 1.
how well each meets the basic functions the chip perimeter to an area over the The perspective view shows a chip with
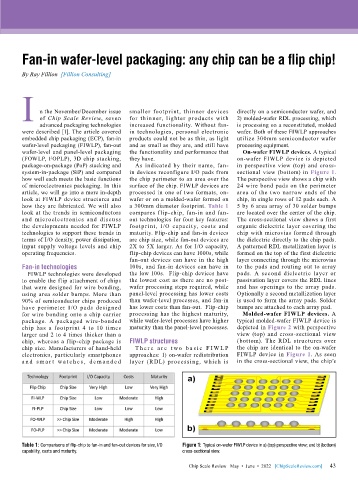
of microelectronics packaging. In this surface of the chip. FIWLP devices are 24 wire bond pads on the perimeter
article, we will go into a more in-depth processed in one of two formats, on- area of the two narrow ends of the
look at FIWLP device structures and wafer or on a molded-wafer formed on chip, in single rows of 12 pads each. A
how they are fabricated. We will also a 300mm diameter footprint. Table 1 5 by 6 area array of 30 solder bumps
look at the trends in semiconductors compares flip-chip, fan-in and fan- are located over the center of the chip.
and microelectronics and discuss out technologies for four key features: The cross-sectional view shows a first
the developments needed for FIWLP footprint, I/O capacity, costs and organic dielectric layer covering the
technologies to support these trends in maturity. Flip-chip and fan-in devices chip with microvias formed through
terms of I/O density, power dissipation, are chip size, while fan-out devices are the dielectric directly to the chip pads.
input supply voltage levels and chip 2X to 5X larger. As for I/O capacity, A patterned RDL metallization layer is
operating frequencies. flip-chip devices can have 1000s, while formed on the top of the first dielectric
fan-out devices can have in the high layer connecting through the microvias
Fan-in technologies 100s, and fan-in devices can have in to the pads and routing out to array
FIWLP technologies were developed the low 100s. Flip-chip devices have pads. A second dielectric layer or
to enable the flip attachment of chips the lowest cost as there are no post- passivation layer covers the RDL lines
that were designed for wire bonding, wafer processing steps required, while and has openings to the array pads.
using area solder bumps. More than panel-level processing has lower costs Optionally a second metallization layer
90% of semiconductor chips produced than wafer-level processes, and fan-in is used to form the array pads. Solder
have perimeter I/O pads designed has lower costs than fan-out. Flip-chip bumps are attached to each array pad.
for wire bonding onto a chip carrier processing has the highest maturity, Molded-wafer FIWLP devices. A
package. A packaged wire-bonded while wafer-level processes have higher typical molded-wafer FIWLP device is
chip has a footprint 4 to 10 times maturity than the panel-level processes. depicted in Figure 2 with perspective
larger and 2 to 4 times thicker than a view (top) and cross-sectional view
chip, whereas a flip-chip package is FIWLP structures (bottom). The RDL structures over
chip size. Manufacturers of hand-held T h e r e a r e t w o b a s i c F I W L P the chip are identical to the on-wafer
electronics, particularly smartphones approaches: 1) on-wafer redistribution FIWLP device in Figure 1. As seen
a nd s m a r t w a t c h e s , d e m a nd e d layer (RDL) processing, which is in the cross-sectional view, the chip’s
Table 1: Comparisons of flip-chip to fan-in and fan-out devices for size, I/O Figure 1: Typical on-wafer FIWLP device in a) (top) perspective view; and b) (bottom)
capability, costs and maturity. cross-sectional view.
43
Chip Scale Review May • June • 2022 [ChipScaleReview.com] 43