Page 41 - Chip Scale Review_May June_2022-digital
P. 41
HDI substrate, can also be combined
through an interconnect layer [12] into
a hybrid substrate. This is very similar
to [11] except the C4 solder joint and
underfill are replaced by an interconnect
layer as shown in Figure 8. For more
information on the design, materials,
process, fabrication, and reliability of
the heterogeneous integration of three
chips on a hybrid substrate with an
interconnect layer by a fan-out RDL-
first panel-level package, please read
[12]. Again, Chip1 could be a SoC and
Chip2A and Chip2B could be memories
or memory cubes.
Heterogeneous integration of EIC
and PIC devices
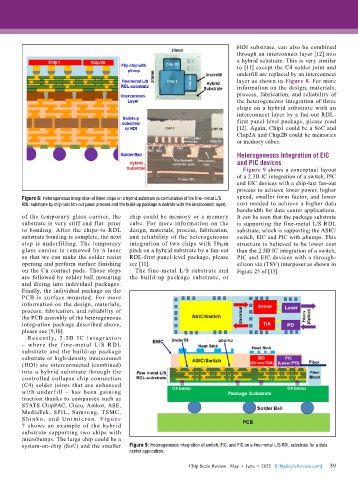
Figure 9 shows a conceptual layout
of a 2.3D IC integration of a switch, PIC
and EIC devices with a chip-last fan-out
process to achieve lower power, higher
Figure 8: Heterogeneous integration of three chips on a hybrid substrate (a combination of the fine-metal L/S speed, smaller form factor, and lower
RDL-substrate by chip-last fan-out panel process and the build-up package substrate with the interconnect layer). cost needed to achieve a higher data
bandwidth for data center applications.
of the temporary glass carrier, the chip could be memory or a memory It can be seen that the package substrate
substrate is very stiff and flat prior cube. For more information on the is supporting the fine-metal L/S RDL
to bonding. After the chips-to-RDL design, materials, process, fabrication, substrate, which is supporting the ASIC/
substrate bonding is complete, the next and reliability of the heterogeneous switch, EIC and PIC with µbumps. This
step is underfilling. The temporary integration of two chips with 50µm structure is believed to be lower cost
glass carrier is removed by a laser pitch on a hybrid substrate by a fan-out than the 2.5D IC integration of a switch,
so that we can make the solder resist RDL-first panel-level package, please PIC and EIC devices with a through-
opening and perform surface finishing see [11]. silicon via (TSV) interposer as shown in
on the Cu contact pads. Those steps The fine-metal L/S substrate and Figure 25 of [13].
are followed by solder ball mounting the build-up package substrate, or
and dicing into individual packages.
Finally, the individual package on the
PCB is surface mounted. For more
information on the design, materials,
process, fabrication, and reliability of
the PCB assembly of the heterogeneous
integration package described above,
please see [9,10].
Re ce ntly, 2.3D IC i nt eg r at ion
– where the f ine-metal L/S R DL
substrate and the build-up package
substrate or high-density interconnect
(HDI) are interconnected (combined)
into a hybrid substrate through the
controlled collapse chip connection
(C4) solder joints that are enhanced
with underfill – has been gaining
traction thanks to companies such as
STATS ChipPAC, Cisco, Amkor, ASE,
MediaTek, SPIL, Samsung, TSMC,
Sh i n ko, a nd Un i m ic ron. F i g ure
7 shows an example of the hybrid
substrate supporting two chips with
microbumps. The large chip could be a
system-on-chip (SoC) and the smaller Figure 9: Heterogeneous integration of switch, EIC, and PIC on a fine-metal L/S RDL substrate for a data
center application.
39
Chip Scale Review May • June • 2022 [ChipScaleReview.com] 39