Page 39 - Chip Scale Review_May June_2022-digital
P. 39
the photoresist, using LDI and then
developing the photoresist, and then
using ECD to deposit the Cu. These
steps are followed by stripping off the
photoresist and etching off the TiCu
seed layer to get the ML (ML2) of
RDL2. Next comes slit coating a PID
and LDI to get the DL (DL12) of RDL2.
The same process steps are repeated to
obtain the ML (ML1) and DL (DL01)
of RDL1. Next comes sputtering the
Ti/Cu, slit coating the photoresist, LDI
and develop, and using ECD to deposit
the Cu. Those steps are followed
by stripping off the photoresist and
etching off the TiCu to get the bonding
pad (lead) for the chips. The last step
in the fabrication of the RDL substrate
immediately before the chips-to-
subst rate bonding is the su rface
finishing of the Cu bonding pads.
Electroless palladium and immersion
gold (EPIG) surface finishing is used.
The fabrication of the fine-metal L/S
RDL substrate is thereby completed.
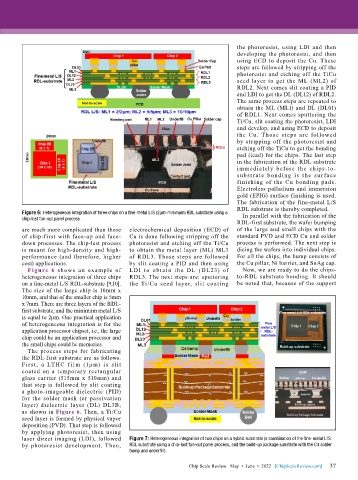
Figure 6: Heterogeneous integration of three chips on a fine-metal L/S (2μm-minimum) RDL substrate using a In parallel with the fabrication of the
chip-last fan-out panel process.
RDL-first substrate, the wafer bumping
are much more complicated than those electrochemical deposition (ECD) of of the large and small chips with the
of chip-first with face-up and face- Cu is done following stripping off the standard PVD and ECD Cu and solder
down processes. The chip-last process photoresist and etching off the Ti/Cu process is performed. The next step is
is meant for high-density and high- to obtain the metal layer (ML) ML3 dicing the wafers into individual chips.
performance (and therefore, higher of RDL3. Those steps are followed For all the chips, the bump consists of
cost) applications. by slit coating a PID and then using the Cu pillar, Ni barrier, and SnAg cap.
Figure 6 shows an example of LDI to obt ai n the DL (DL23) of Now, we are ready to do the chips-
heterogeneous integration of three chips RDL3. The next steps are: sputtering to-RDL substrate bonding. It should
on a fine-metal L/S RDL-substrate [9,10]. the Ti/Cu seed layer, slit coating be noted that, because of the support
The size of the large chip is 10mm x
10mm, and that of the smaller chip is 5mm
x 7mm. There are three layers of the RDL-
first substrate, and the minimum metal L/S
is equal to 2μm. One practical application
of heterogeneous integration is for the
application processor chipset, i.e., the large
chip could be an application processor and
the small chips could be memories.
The process steps for fabricating
the RDL-first substrate are as follows.
Fi rst, a LTHC f il m (1μ m) is slit
coated on a temporary rectangular
glass carrier (515mm x 510mm) and
that step is followed by slit coating
a photo-imageable dielectric (PID)
for the solder mask (or passivation
layer) dielectric layer (DL) DL3B,
as shown in Figure 6. Then, a Ti/Cu
seed layer is formed by physical vapor
deposition (PVD). That step is followed
by applying photoresist, then using
laser direct imaging (LDI), followed Figure 7: Heterogeneous integration of two chips on a hybrid substrate (a combination of the fine-metal L/S
by photoresist development. Then, RDL substrate using a chip-last fan-out panel process, and the build-up package substrate with the C4 solder
bump and underfill).
37
Chip Scale Review May • June • 2022 [ChipScaleReview.com] 37