Page 56 - ChipScale_Mar-Apr_2021-digital
P. 56
shape (smiling or frowning). The warpage
profiles change depending on several
factors such as silicon to mold density, die
shape (i.e., square and rectangular), number
of RDLs, and specifically for the panel
format, the chip layout plays a significant
factor (Figure 2).
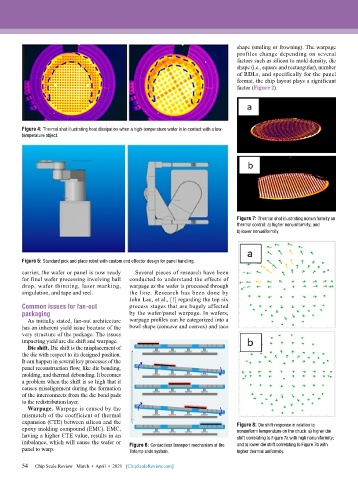
Figure 4: Thermal shot illustrating heat dissipation when a high-temperature wafer is in contact with a low-
temperature object.
Figure 7: Thermal shot illustrating nonuniformity on
thermal control: a) higher nonuniformity; and
b) lower nonuniformity.
Figure 5: Standard pick and place robot with custom end effector design for panel handling.
carrier, the wafer or panel is now ready Several pieces of research have been
for final wafer processing involving ball conducted to understand the effects of
drop, wafer thinning, laser marking, warpage as the wafer is processed through
singulation, and tape and reel. the line. Research has been done by
John Lau, et al., [1] regarding the top six
Common issues for fan-out process stages that are hugely affected
packaging by the wafer/panel warpage. In wafers,
As initially stated, fan-out architecture warpage profiles can be categorized into a
has an inherent yield issue because of the bowl shape (concave and convex) and taco
very structure of the package. The issues
impacting yield are die shift and warpage.
Die shift. Die shift is the misplacement of
the die with respect to its designed position.
It can happen in several key processes of the
panel reconstruction flow, like die bonding,
molding, and thermal debonding. It becomes
a problem when the shift is so high that it
causes misalignment during the formation
of the interconnects from the die bond pads
to the redistribution layer.
Warpage. Warpage is caused by the
mismatch of the coefficient of thermal
expansion (CTE) between silicon and the
epoxy molding compound (EMC). EMC, Figure 8: Die shift response in relation to
nonuniform temperature on the chuck: a) higher die
having a higher CTE value, results in an shift correlating to Figure 7a with high nonuniformity;
imbalance, which will cause the wafer or and b) lower die shift correlating to Figure 7b with
panel to warp. Figure 6: Contactless transport mechanism of the higher thermal uniformity.
Tritemp slide system.
54
54 Chip Scale Review March • April • 2021 [ChipScaleReview.com]