Page 41 - ChipScale_Sep-Oct_2020-digital
P. 41
Formic acid reduction mechanism. oxide layers on solder and metal
The chemical reactions through which surfaces prior to and/or during the TCB
formic acid vapor reduces the Sn or Cu process. The middle channel serves as
surface are given in (1), (2) and [11-13]. an exhaust collection port for residual
FA vapor and other gaseous reaction
byproducts. The outermost channel
provides the shielding N 2 gas around
the shroud. This helps to maximize the
FA in vapor form reacts with the containment of residual FA vapor and
tin oxide and leaves a thin layer of tin other reaction by-products under the
formate. This formate layer covers the shroud area. The escaped FA vapors,
bare solder surface and is subsequently inside the machine environment,
r e move d by r a i si ng t he s u r fa c e are ultimately expelled through the Figure 2: A bond head shroud.
temperature above 150°C. A very similar facility-provided exhaust system,
chemical reaction also happens for the which, along with the FA concentration
copper oxide reduction process [5]. inside the machine, is continuously
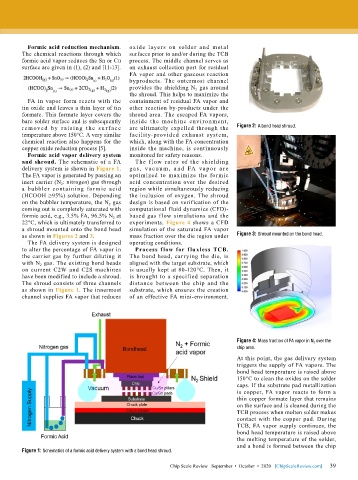
Formic acid vapor delivery system monitored for safety reasons.
and shroud. The schematic of a FA The f low rates of the shielding
delivery system is shown in Figure 1. g a s , va c uu m , a nd FA vap or a r e
The FA vapor is generated by passing an optimized to maximize the formic
inert carrier (N 2 : nitrogen) gas through acid concentration over the desired
a bubbler containing for mic acid region while simultaneously reducing
(HCOOH ≥95%) solution. Depending the inclusion of oxygen. The shroud
on the bubbler temperature, the N 2 gas design is based on verification of the
coming out is completely saturated with computational fluid dynamics (CFD)-
formic acid, e.g., 3.5% FA, 96.5% N 2 at based gas flow simulations and the
22°C, which is ultimately transferred to experiments. Figure 4 shows a CFD
a shroud mounted onto the bond head simulation of the saturated FA vapor
as shown in Figures 2 and 3. mass fraction over the die region under Figure 3: Shroud mounted on the bond head.
The FA delivery system is designed operating conditions.
to alter the percentage of FA vapor in Process f low for f luxless TCB.
the carrier gas by further diluting it The bond head, carrying the die, is
with N 2 gas. The existing bond heads aligned with the target substrate, which
on current C2W and C2S machines is usually kept at 80-120°C. Then, it
have been modified to include a shroud. is brought to a specified separation
The shroud consists of three channels distance between the chip and the
as shown in Figure 1. The innermost substrate, which ensures the creation
channel supplies FA vapor that reduces of an effective FA mini-environment.
Figure 4: Mass fraction of FA vapor in N 2 over the
chip area.
At this point, the gas delivery system
triggers the supply of FA vapors. The
bond head temperature is raised above
150°C to clean the oxides on the solder
caps. If the substrate pad metallization
is copper, FA vapor reacts to form a
thin copper formate layer that remains
on the surface and is cleaned during the
TCB process when molten solder makes
contact with the copper pad. During
TCB, FA vapor supply continues, the
bond head temperature is raised above
the melting temperature of the solder,
and a bond is formed between the chip
Figure 1: Schematics of a formic acid delivery system with a bond head shroud.
39
Chip Scale Review September • October • 2020 [ChipScaleReview.com] 39