Page 20 - Chip Scale Review_March-April_2024-digital
P. 20
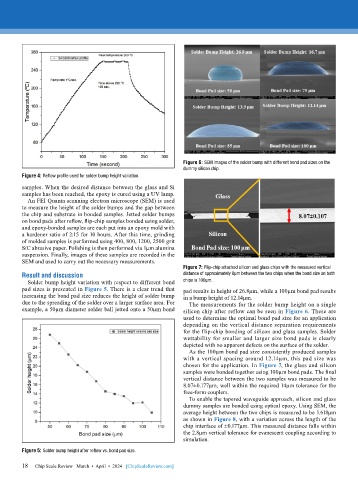
Figure 6: SEM images of the solder bump with different bond pad sizes on the
dummy silicon chip.
Figure 4: Reflow profile used for solder bump height variation.
samples. When the desired distance between the glass and Si
samples has been reached, the epoxy is cured using a UV lamp.
An FEI Quanta scanning electron microscope (SEM) is used
to measure the height of the solder bumps and the gap between
the chip and substrate in bonded samples. Jetted solder bumps
on bond pads after reflow, flip-chip samples bonded using solder,
and epoxy-bonded samples are each put into an epoxy mold with
a hardener ratio of 2:15 for 10 hours. After this time, grinding
of molded samples is performed using 400, 800, 1200, 2500 grit
SiC abrasive paper. Polishing is then performed via 1µm alumina
suspension. Finally, images of these samples are recorded in the
SEM and used to carry out the necessary measurements.
Figure 7: Flip-chip attached silicon and glass chips with the measured vertical
Result and discussion distance of approximately 8µm between the two chips when the bond size on both
Solder bump height variation with respect to different bond chips is 100µm.
pad sizes is presented in Figure 5. There is a clear trend that pad results in height of 26.8µm, while a 100µm bond pad results
increasing the bond pad size reduces the height of solder bump in a bump height of 12.14µm.
due to the spreading of the solder over a larger surface area. For The measurements for the solder bump height on a single
example, a 50µm diameter solder ball jetted onto a 50µm bond silicon chip after reflow can be seen in Figure 6. These are
used to determine the optimal bond pad size for an application
depending on the vertical distance separation requirements
for the flip-chip bonding of silicon and glass samples. Solder
wettability for smaller and larger size bond pads is clearly
depicted with no apparent defects on the surface of the solder.
As the 100µm bond pad size consistently produced samples
with a vertical spacing around 12.14µm, this pad size was
chosen for the application. In Figure 7, the glass and silicon
samples were bonded together using 100µm bond pads. The final
vertical distance between the two samples was measured to be
8.07±0.177µm, well within the required 14µm tolerance for the
free-form couplers.
To enable the tapered waveguide approach, silicon and glass
dummy samples are bonded using optical epoxy. Using SEM, the
average height between the two chips is measured to be 1.618µm
as shown in Figure 8, with a variation across the length of the
chip interface of ±0.177µm. This measured distance falls within
the 2.8µm vertical tolerance for evanescent coupling according to
simulation.
Figure 5: Solder bump height after reflow vs. bond pad size.
18 Chip Scale Review March • April • 2024 [ChipScaleReview.com]
18