Page 22 - Chip Scale Review_January-February_2024-digital
P. 22
• Provides various low-cost multi-
chip read-out IC (ROIC) assembly
for silicon avalanche photodiodes
(Si-APDs) and other imagers [15-17].
• Introduces flip-chip Si-less active/
passive bridge for chip-to-chip
connection.
• Enables a thermally-optimized Si
floorplan.
• Provides a cost benefit for yield and
node optimization.
Summary
An integrated approach to develop
ELAICs, or “megachips,” using various
heterogeneous die configurations has
been demonstrated. This approach
is suitable for high-end, expensive
electronics where an SoC can be
divided into chiplets with desired
functionality and an ELAIC multi-
die SoC can be created. The ELAIC
can incorporate chips/chiplets from
different foundr y processes, and
different technology nodes to improve
mix and match capability, which
further improves package performance.
It also provides scalability to place a
large number of chips onto the ELAIC
platform, and enables a design that
packages many different functionalities
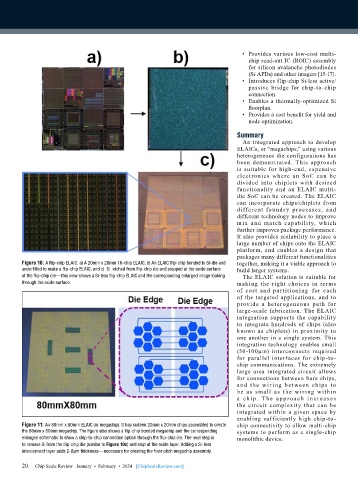
Figure 10: A flip-chip ELAIC: a) A 20mm x 20mm 16-chip ELAIC; b) An ELAIC flip-chip bonded to Si-die and together, making it a viable approach to
underfilled to make a flip-chip ELAIC; and c) Si etched from flip-chip die and stopped at the oxide surface build larger systems.
of the flip-chip die—this view shows a Si-less flip-chip ELAIC and the corresponding enlarged image looking The ELAIC solution is suitable for
through the oxide surface. making the right choices in terms
of cost and partitioning–for each
of the targeted applications, and to
provide a heterogeneous path for
large-scale fabrication. The ELAIC
integration supports the capability
to integrate hundreds of chips (also
known as chiplets) in proximity to
one another in a single system. This
integration technology enables small
(50-100µm) interconnects required
for parallel interfaces for chip-to-
chip communications. The extremely
large area integrated circuit allows
for connections between bare chips,
and the wir ing bet ween chips to
be as small as the wiring within
a ch ip. T he a p p r oa ch i nc r e a s e s
the circuit complexity that can be
integrated within a given space by
enabling sufficiently high chip-to-
Figure 11: An 80mm x 80mm ELAIC (or megachip). It has sixteen 20mm x 20mm chips assembled to create chip connectivity to allow multi-chip
the 80mm x 80mm megachip. The figure also shows a flip-chip bonded megachip and the corresponding systems to perform as a single-chip
enlarged schematic to show a chip-to-chip connection option through the flip-chip die. The next step is monolithic device.
to remove Si from the flip-chip die (similar to Figure 10c) and stop at the oxide layer. Adding a Si-less
interconnect layer adds 2-6µm thickness—necessary for creating the finer pitch megachip assembly.
20
20 Chip Scale Review January • February • 2024 [ChipScaleReview.com]