Page 23 - Chip Scale Review_November-December_2023-digital
P. 23
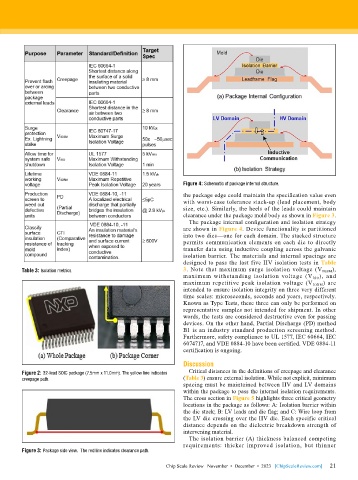
Figure 4: Schematic of package internal structure.
the package edge could maintain the specification value even
with worst-case tolerance stack-up (lead placement, body
size, etc.). Similarly, the heels of the leads could maintain
clearance under the package mold body as shown in Figure 3.
The package internal configuration and isolation strategy
are shown in Figure 4. Device functionality is partitioned
into two dies—one for each domain. The stacked structure
permits communication elements on each die to directly
transfer data using inductive coupling across the galvanic
isolation barrier. The materials and internal spacings are
designed to pass the last five HV isolation tests in Table
Table 3: Isolation metrics. 3. Note that maximum surge isolation voltage (V IOSM ),
maximum withstanding isolation voltage (V ISO ), and
maximum repetitive peak isolation voltage (V IORM ) are
intended to ensure isolation integrity on three very different
time scales: microseconds, seconds and years, respectively.
Known as Type Tests, these three can only be performed on
representative samples not intended for shipment. In other
words, the tests are considered destructive even for passing
devices. On the other hand, Partial Discharge (PD) method
B1 is an industry standard production screening method.
Furthermore, safety compliance to UL 1577, IEC 60664, IEC
6074717, and VDE 0884-10 have been certified. VDE 0884-11
certification is ongoing.
Discussion
Figure 2: 32-lead SOIC package (7.5mm x 11.0mm). The yellow line indicates Critical distances in the definitions of creepage and clearance
creepage path. (Table 3) ensure external isolation. While not explicit, minimum
spacing must be maintained between HV and LV domains
within the package to pass the internal isolation requirements.
The cross section in Figure 5 highlights three critical geometry
locations in the package as follows: A: Isolation barrier within
the die stack; B: LV leads and die flag; and C: Wire loop from
the LV die crossing over the HV die. Each specific critical
distance depends on the dielectric breakdown strength of
intervening material.
The isolation barrier (A) thickness balanced competing
requirements: thicker improved isolation, but thinner
Figure 3: Package side view. The red line indicates clearance path.
21
Chip Scale Review November • December • 2023 [ChipScaleReview.com] 21