Page 47 - Chip Scale Review_September-October_2023-digital
P. 47
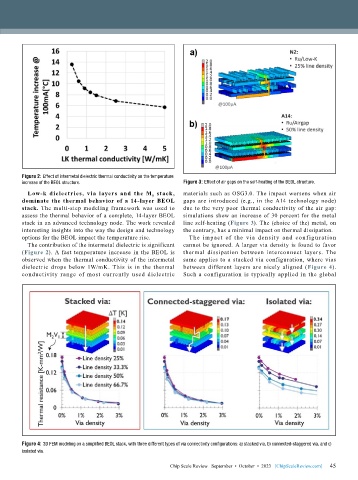
Figure 2: Effect of intermetal dielectric thermal conductivity on the temperature
increase of the BEOL structure. Figure 3: Effect of air gaps on the self-heating of the BEOL structure.
Low-k dielectrics, via layers and the M y stack, materials such as OSG3.0. The impact worsens when air
dominate the thermal behavior of a 14-layer BEOL gaps are introduced (e.g., in the A14 technology node)
stack. The multi-step modeling framework was used to due to the very poor thermal conductivity of the air gap:
assess the thermal behavior of a complete, 14-layer BEOL simulations show an increase of 30 percent for the metal
stack in an advanced technology node. The work revealed line self-heating (Figure 3). The (choice of the) metal, on
interesting insights into the way the design and technology the contrary, has a minimal impact on thermal dissipation.
options for the BEOL impact the temperature rise. The impact of the via density and conf iguration
The contribution of the intermetal dielectric is significant cannot be ignored. A larger via density is found to favor
(Figure 2). A fast temperature increase in the BEOL is thermal dissipation between interconnect layers. The
observed when the thermal conductivity of the intermetal same applies to a stacked via configuration, where vias
dielectric drops below 1W/mK. This is in the thermal between different layers are nicely aligned (Figure 4).
conductivity range of most currently used dielectric Such a configuration is typically applied in the global
Figure 4: 3D FEM modeling on a simplified BEOL stack, with three different types of via connectivity configurations: a) stacked via, b) connected-staggered via, and c)
isolated via.
45
Chip Scale Review September • October • 2023 [ChipScaleReview.com] 45