Page 15 - Chip Scale Review_September-October_2023-digital
P. 15
Many wafers cannot be tested at all using be tested with two insertions: you test one wafer dies: instead of moving the wafer
standard prober architectures that involve side first, then you flip the wafer and test under a probe card that is docked to the
a wafer prober where the wafer is docked the opposite side. Conversely, a wafer with tester—as it is commonly done on every
on a chuck, and a probe card that is docked pass-through dies cannot be tested at all. test floor—we have developed a prober
to the tester positioned on the top of the To enable the adoption of these architecture able to move multiple mobile
wafer. If you have uneven geometries on technologies and designs, new test probe cards over the wafer surface. This
the wafer, the conventional way of probing methodologies are being developed to new technology combines our experience
the wafer with a probe card is not viable leverage probing technologies that enable in both flying probe technology and mixed-
because the probe card requires all the dies higher parallelism and lower the cost of signal testing. With this new technology,
with the same shape and orientation. If you test, while meeting the rapidly evolving up to eight different small probe cards (four
have different dies with different shapes on technical challenges posed by trends in IC on the top, and four on the bottom side)
a MPW, you also cannot use a traditional design and manufacturing. can be equipped simultaneously on our
prober unless you change the probe card TH2000 prober. Each one is mounted on
to test different parts of the wafer with Overturning the concept of probing an independent robotic axis that moves in
multiple insertions. As for the wafers that An alternative approach to probing the X, Y and Z directions (Figure 4).
have dies mounted on both sides, they can consists in inverting the way you probe
Testing wafers with varied
geometries
Each of the eight probe cards on our
new prober can have a different design,
adapting to different die shape or pitch,
including unconventional and high-
density geometries. This design feature
extends the range of applications that can
be fully tested at the wafer level.
With a single prober insertion, it is
possible to: 1) perform both control
pattern test and pad test; 2) test MPWs,
dedicating a probe card to each specific
device layout; and 3) test wafers with
uneven geometries (e.g., with mirrored
or rotated layout for the different dies).
In all these cases, each probe card fulfills
a specific test function, with a proper
probing layout, working on the whole
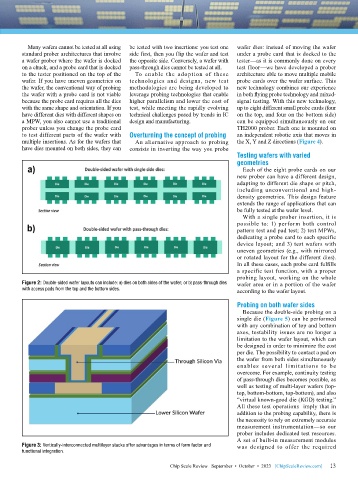
Figure 2: Double-sided wafer layouts can include: a) dies on both sides of the wafer; or b) pass-through dies wafer area or in a portion of the wafer
with access pads from the top and the bottom sides. according to the wafer layout.
Probing on both wafer sides
Because the double-side probing on a
single die (Figure 5) can be performed
with any combination of top and bottom
axes, testability issues are no longer a
limitation to the wafer layout, which can
be designed in order to minimize the cost
per die. The possibility to contact a pad on
the wafer from both sides simultaneously
enables several limitations to be
overcome. For example, continuity testing
of pass-through dies becomes possible, as
well as testing of multi-layer wafers (top-
top, bottom-bottom, top-bottom), and also
“virtual known-good die (KGD) testing.”
All these test operations imply that in
addition to the probing capability, there is
the necessity to rely on extremely accurate
measurement instrumentation—so our
prober includes dedicated test resources.
A set of built-in measurement modules
Figure 3: Vertically-interconnected multilayer stacks offer advantages in terms of form factor and was designed to offer the required
functional integration.
13
Chip Scale Review September • October • 2023 [ChipScaleReview.com] 13