Page 24 - Chip Scale Review_November December_2022-digital
P. 24
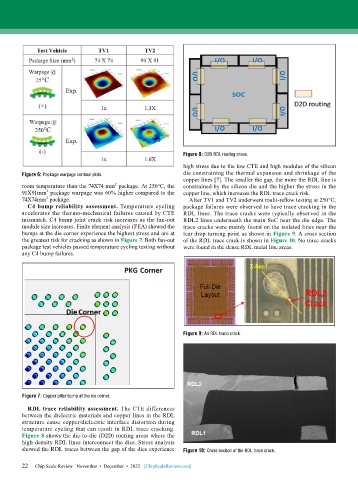
Figure 8: D2D RDL routing areas.
high stress due to the low CTE and high modulus of the silicon
Figure 6: Package warpage contour plots. die constraining the thermal expansion and shrinkage of the
copper lines [7]. The smaller the gap, the more the RDL line is
2
room temperature than the 74X74 mm package. At 250°C, the constrained by the silicon die and the higher the stress in the
2
91X91mm package warpage was 60% higher compared to the copper line, which increases the RDL trace crack risk.
2
74X74mm package. After TV1 and TV2 underwent multi-reflow testing at 250°C,
C4 bump reliability assessment. Temperature cycling package failures were observed to have trace cracking in the
accelerates the thermo-mechanical failures caused by CTE RDL lines. The trace cracks were typically observed in the
mismatch. C4 bump joint crack risk increases as the fan-out RDL2 lines underneath the main SoC near the die edge. The
module size increases. Finite element analysis (FEA) showed the trace cracks were mainly found on the isolated lines near the
bumps at the die corner experience the highest stress and are at tear drop turning point as shown in Figure 9. A cross section
the greatest risk for cracking as shown in Figure 7. Both fan-out of the RDL trace crack is shown in Figure 10. No trace cracks
package test vehicles passed temperature cycling testing without were found in the dense RDL metal line areas.
any C4 bump failures.
Figure 9: An RDL trace crack.
Figure 7: Copper pillar bump at the die corner.
RDL trace reliability assessment. The CTE differences
between the dielectric materials and copper lines in the RDL
structure cause copper/dielectric interface distortion during
temperature cycling that can result in RDL trace cracking.
Figure 8 shows the die-to-die (D2D) routing areas where the
high-density RDL lines interconnect the dies. Stress analysis
showed the RDL traces between the gap of the dies experience Figure 10: Cross section of the RDL trace crack.
22
22 Chip Scale Review November • December • 2022 [ChipScaleReview.com]