Page 23 - Chip Scale Review_January February_2022-digital
P. 23
Bridges for chiplet design and heterogeneous
integration packaging
By John H. Lau [Unimicron Technology Corporation]
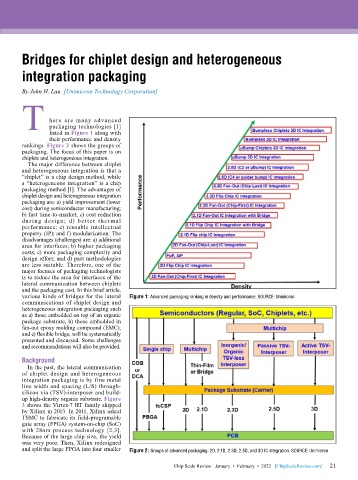
T here are many advanced
packaging technologies [1]
listed in Figure 1 along with
their performance and density
rankings. Figure 2 shows the groups of
packaging. The focus of this paper is on
chiplets and heterogeneous integration.
The major difference between chiplet
and heterogeneous integration is that a
“chiplet” is a chip design method, while
a “heterogeneous integration” is a chip
packaging method [1]. The advantages of
chiplet design and heterogeneous integration
packaging are: a) yield improvement (lower
cost) during semiconductor manufacturing;
b) fast time-to-market; c) cost reduction
dur ing desig n; d) bet ter ther mal
performance; e) reusable intellectual
property (IP); and f) modularization. The
disadvantages (challenges) are: a) additional
area for interfaces; b) higher packaging
costs; c) more packaging complexity and
design effort; and d) past methodologies
are less suitable. Therefore, one of the
major focuses of packaging technologists
is to reduce the area for interfaces of the
lateral communication between chiplets
and the packaging cost. In this brief article,
various kinds of bridges for the lateral Figure 1: Advanced packaging ranking in density and performance. SOURCE: Unimicron
communications of chiplet design and
heterogeneous integration packaging such
as a) those embedded on top of an organic
package substrate, b) those embedded in
fan-out epoxy molding compound (EMC),
and c) flexible bridge, will be systematically
presented and discussed. Some challenges
and recommendations will also be provided.
Background
In the past, the lateral communication
of chiplet design and heterogeneous
integration packaging is by fine metal
line width and spacing (L/S) through-
silicon via (TSV)-interposer and build-
up high-density organic substrate. Figure
3 shows the Virtex-7 HT family shipped
by Xilinx in 2013. In 2011, Xilinx asked
TSMC to fabricate its field-programable
gate array (FPGA) system-on-chip (SoC)
with 28nm process technology [2,3].
Because of the large chip size, the yield
was very poor. Then, Xilinx redesigned
and split the large FPGA into four smaller Figure 2: Groups of advanced packaging: 2D, 2.1D, 2.3D, 2.5D, and 3D IC integration. SOURCE: Unimicron
21
Chip Scale Review January • February • 2022 [ChipScaleReview.com] 21