Page 26 - ChipScale_Jan-Feb_2020-digital
P. 26
at the slope, one can expect this to
continue close to linearly, indicating that
increasing the number of pixels by using
a higher resolution camera setup enables
one to reach the optical lateral resolution
limitation of the system (4.875µm) [5].
Table 2: Specifications for the 2 mirrors reported in this paper. All mirrors were 50.8mm in diameter with
aluminum coating.
Z-height resolution: amplitude
A key aspect in determining the over the sample using a lens that exhibits analyzer. Any light coming from out-of-
m i n i mu m a mplit ude t hat ca n be a large longitudinal chromatic aberration focus reflections will be rejected by the
measured by a system is the noise [9]. Because the chromatic aberration pinhole aperture. Finally, by detecting the
level. The noise level for AFM is about causes different wavelengths to focus at peak wavelength, the sample position can
0.1nm and the noise level for an optical different heights, there will be a specific be found.
profiler is on the order of 0.4nm. wavelength (λ 0 ), for which the focus lies The technique described above has
However, both techniques struggle on the surface sample. The reflected light been used in metrology because of its
with speed and a very small field of from the sample passes back through capacity of measuring a large variety of
view [8]. the lens and is derived using a spectrum surfaces. Its main limitation comes from
A noise simulation was done where
two circular images were generated
and noise levels ranged from 20dB to
infinity (meaning infinite exposure
time). The two noisy images were
then put into the WFPI measurement
algorithm and analyzed as if the two
images had been acquired using the
WFPI system. The noise is given in
nanometer root-mean-square (RMS)
with its standard deviation (σ). The
noise level is summarized in Figure 5.
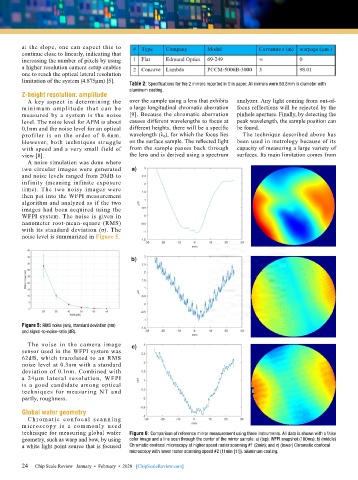
Figure 5: RMS noise (nm), standard deviation (nm)
and signal-to-noise-ratio (dB).
The noise in the camera image
sensor used in the WFPI system was
62dB, which translated to an RMS
noise level at 0.3nm with a standard
deviation of 0.1nm. Combined with
a 24µm lateral resolution, W FPI
is a good candidate among optical
techniques for measuring NT and
partly, roughness.
Global wafer geometry
C h r o m a t ic c o n fo c a l s c a n n i ng
m icroscopy is a com mon ly used
technique for measuring global wafer Figure 6: Comparison of reference mirror measurement using three instruments. All data is shown with a false
geometry, such as warp and bow, by using color image and a line scan through the center of the mirror sample. a) (top): WFPI snapshot (100ms); b) (middle)
a white light point source that is focused Chromatic confocal microscopy at higher speed raster scanning #1 (2min); and c) (lower) Chromatic confocal
microscopy with lower raster scanning speed #2 (11min [11]). aluminum coating.
24
24 Chip Scale Review January • February • 2020 [ChipScaleReview.com]