Page 24 - ChipScale_Jan-Feb_2020-digital
P. 24
slope, which also depends on d and on gravity. The specifications of the system T-22-2-N-CG). This test target comprises
2
the pixel size n given by r max =n ⁄(4∙d). It are summarized in Table 1 [4] (also, a glass substrate with a deposition of
is worth noting that for a given imaging see Figure 3). chrome that forms line pairs with lateral
sensor, the maximum range and the height frequencies up to 512 cycles per mm
resolution can be modified by varying (cy/mm), one cycle being 2 pixels side-
the distance between measurement by-side with different contrast ratios.
planes. For instance, it may seem that by Because the chrome deposition layer
increasing d, the resolution can improve creates surface topography, it can be
indefinitely. The limit for the distance d is used to measure the performance of
defined by the range in which geometrical WFPI in terms of lateral resolution. The
optics are still valid. The Fresnel number process consisted of placing the test
is widely accepted as an indicator of target in the WFPI measurement system
2
optical range given by F=r ⁄(L∙λ) where and running a single measurement of
r is the aperture radius, L denotes the an area that contains line groups with
propagation distance and λ represents spatial frequencies in a range valid for
the wavelength of the light. When F >> 1 this study [5].
the range is considered geometrical. We On account of the two cameras and
have empirically found that a value of F the magnification of the telecentric
≥ 100 guarantees the correct working of lens arrangement used, the pixel size
WFPI. This condition sets the maximum in object space is 24µm (Table 1.),
value that the propagation distance which translated to a frequency that is
2
can take (L max ≤ r ⁄(100∙λ)), in WFPI, equivalent to approximately 20cy/mm
the maximum propagation distance (1mm⁄((2×24μm)≈20). A phase image of
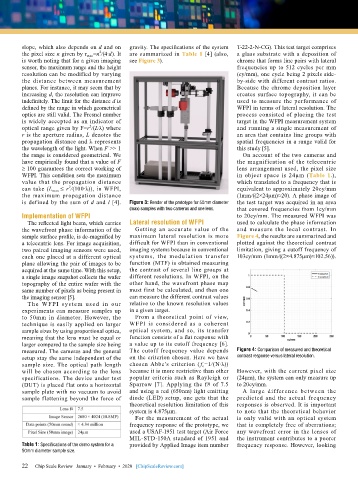
is defined by the sum of d and l [4]. Figure 3: Render of the prototype for 50mm diameter the test target was acquired in an area
(max) samples with two cameras and one lens. that covered frequencies from 1cy/mm
Implementation of WFPI to 20cy/mm. The measured WFPI was
The reflected light beam, which carries Lateral resolution of WFPI used to calculate the phase information
the wavefront phase information of the Getting an accurate value of the and measure the local contrast. In
sample surface profile, is de-magnified by maximum lateral resolution is more Figure 4, the results are summarized and
a telecentric lens. For image acquisition, difficult for WFPI than in conventional plotted against the theoretical contrast
two paired imaging sensors were used, imaging systems because in conventional limitation, giving a cutoff frequency of
each one placed at a different optical systems, the modulation transfer 103cy/mm (1mm⁄((2×4.875μm)≈102.56)).
plane allowing the pair of images to be function (MTF) is obtained measuring
acquired at the same time. With this setup, the contrast of several line groups at
a single image snapshot collects the wafer different resolutions. In WFPI, on the
topography of the entire wafer with the other hand, the wavefront phase map
same number of pixels as being present in must first be calculated, and then one
the imaging sensor [5]. can measure the different contrast values
T he W F PI system u sed i n ou r relative to the known resolution values
experiments can measure samples up in a given target.
to 50mm in diameter. However, the From a theoretical point of view,
technique is easily applied on larger WFPI is considered as a coherent
sample sizes by using proportional optics, optical system, and so, its transfer
meaning that the lens must be equal or function consists of a flat response with
larger compared to the sample size being a value up to its cutoff frequency [6].
measured. The cameras and the general The cutoff frequency value depends Figure 4: Comparison of measured and theoretical
setup stay the same independent of the on the criterion chosen. Here we have contrast response versus lateral resolution.
sample size. The optical path length chosen Abbe’s criterion ( f c =1⁄(N∙λ))
will be chosen according to the lens because it is more restrictive than other However, with the current pixel size
specifications. The device under test popular criteria such as Rayleigh or (24µm), the system can only measure up
(DUT) is placed flat onto a horizontal Sparrow [7]. Applying the f# of 7.5 to 20cy/mm.
sample plate with no vacuum to avoid and using a red (650nm) light emitting A large difference between the
sample flattening beyond the force of diode (LED) setup, one gets that the predicted and the actual frequency
theoretical resolution limitation of this responses is observed. It is important
system is 4.875µm. to note that the theoretical behavior
For the measurement of the actual is only valid with an optical system
frequency response of the prototype, we that is completely free of aberrations;
used a USAF-1951 test target (Air Force any wavefront error in the lenses of
MIL-STD-150A standard of 1951 and the instrument contributes to a poorer
Table 1: Specifications of the demo system for a provided by Applied Image item number frequency response. However, looking
50mm diameter sample size.
22 Chip Scale Review January • February • 2020 [ChipScaleReview.com]
22