Page 19 - ChipScale_Jan-Feb_2020-digital
P. 19
placement measurements and pattern It uses pattern recognition alignment,
overlay registration requirements are allowing the user to train the system
continuing to tighten. As a result, the to recognize and align on any unique
position of the die must be measured pattern within the field of view. The
before each exposure in the lithography alignment system can measure the X,
system to ensure accurate registration with Y position of die patterns across the
the underlying layer. Displacement errors panel, a process often referred to as
can be measured in the lithography tool, “mapping.” The AOI system (Firefly
but these measurements are slow, typically System, Onto Innovation) uses a similar
taking as much time as the exposure pattern recognition alignment method
itself. Transferring the measurement to assess die placement error. Using
operation to a parallel, independent the stepper and AOI alignment site
metrology system and feeding corrections measurements from the test vehicle
to the stepper, however, can double panel, a mathematical algorithm was
throughput. Figure 1 illustrates the use applied to align the stepper and AOI
of this exposure/measurement loop to coordinate systems. Once a common
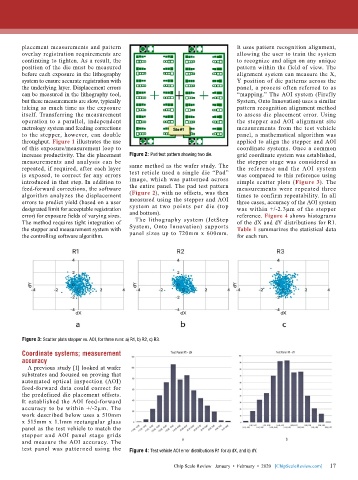
increase productivity. The die placement Figure 2: Pad test pattern showing two die. grid coordinate system was established,
measurements and analysis can be the stepper stage was considered as
repeated, if required, after each layer same method as the wafer study. The the reference and the AOI system
is exposed, to correct for any errors test reticle used a single die “Pad” was compared to this reference using
introduced in that step. In addition to image, which was patterned across simple scatter plots (Figure 3). The
feed-forward corrections, the software the entire panel. The pad test pattern measurements were repeated three
algorithm analyzes the displacement (Figure 2), with no offsets, was then times to confirm repeatability. In all
errors to predict yield (based on a user measured using the stepper and AOI three cases, accuracy of the AOI system
designated limit for acceptable registration system at two points per die (top was within +/-2.3µm of the stepper
error) for exposure fields of varying sizes. and bottom). reference. Figure 4 shows histograms
The method requires tight integration of The lithography system (JetStep of the dX and dY distributions for R1.
the stepper and measurement system with System, Onto Innovation) supports Table 1 summarizes the statistical data
the controlling software algorithm. panel sizes up to 720mm x 600mm. for each run.
Figure 3: Scatter plots stepper vs. AOI, for three runs: a) R1, b) R2, c) R3.
Coordinate systems; measurement
accuracy
A previous study [1] looked at wafer
substrates and focused on proving that
automated optical inspection (AOI)
feed-forward data could correct for
the predefined die placement offsets.
It established the AOI feed-forward
accuracy to be within +/-2µm. The
work described below uses a 510mm
x 515mm x 1.1mm rectangular glass
panel as the test vehicle to match the
stepper and AOI panel stage grids
and measure the AOI accuracy. The
test panel was patterned using the Figure 4: Test vehicle AOI error distributions R1 for a) dX, and b) dY.
17
Chip Scale Review January • February • 2020 [ChipScaleReview.com] 17