Page 14 - ChipScale_Jan-Feb_2020-digital
P. 14
UBM and solder ball fatigue. This slightly shift caused by fatigue will eventually be thickness of the Cu RDL redistribution
different electrical length will cause a less than the specified limit. layer (Figure 9).
small difference in phase Ф(S21) of the One might ask, “How do thermal
insertion loss, which is undesirable in radar Thermal performance measu rements f it to the ther mal
applications. It is therefore important to Typical power consumptions for simulations, and how does the thermal
demonstrate that none of the fatigue modes automotive monolithic microwave behavior change over the lifetime of the
and their combinations lead to a phase shift integrated circuits (MMICs) are in package?” Temperature-driven fatigue
exceeding the specified limit. the range of 1-3W. To remove the heat modes as described above, are leading to a
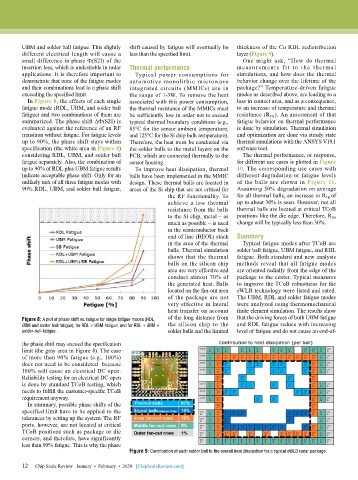
In Figure 8, the effects of each single associated with this power consumption, loss in contact area, and as a consequence,
fatigue mode (RDL, UBM, and solder ball the thermal resistance of the MMICs must to an increase of temperature and thermal
fatigue) and two combinations of them are be sufficiently low in order not to exceed resistance (R TH ). An assessment of that
summarized. The phase shift ΔФ(S21) is typical thermal boundary conditions (e.g., fatigue behavior on thermal performance
evaluated against the reference of an RF 85°C for the sensor ambient temperature, is done by simulation. Thermal simulation
transition without fatigue. For fatigue levels and 125°C for the Si chip bulk temperature). and optimization are done via steady state
up to 90%, the phase shift stays within Therefore, the heat must be conducted via thermal simulations with the ANSYS V19.1
specification (the white area in Figure 8) the solder balls to the metal layers on the software tool.
considering RDL, UBM, and solder ball PCB, which are connected thermally to the The thermal performance, or response,
fatigue separately. Also, the combination of sensor housing. for different use cases is plotted in Figure
up to 90% of RDL plus UBM fatigue results To improve heat dissipation, thermal 10. The corresponding use cases with
indicate acceptable phase shift. Only for an balls have been implemented in the MMIC different degradation or fatigue levels
unlikely mix of all three fatigue modes with design. These thermal balls are located in of the balls are shown in Figure 11.
90% RDL, UBM, and solder ball fatigue, areas of the Si chip that are not critical for Assuming 50% degradation on average
the RF functionality. To for all thermal balls, an increase in R TH of
achieve a low thermal up to about 30% is seen. However, not all
resistance from the balls thermal balls are located at critical TCoB
to the Si chip, metal – as positions like the die edge. Therefore, R TH
much as possible – is used change will be typically less than 30%.
in the semiconductor back
end of line (BEOL) stack Summary
in the area of the thermal Typical fatigue modes after TCoB are
balls. Thermal simulation solder ball fatigue, UBM fatigue, and RDL
shows that the thermal fatigue. Both standard and new analysis
balls on the silicon chip methods reveal that all fatigue modes
area are very effective and are oriented radially from the edge of the
conduct almost 70% of package to the center. Typical measures
the generated heat. Balls to improve the TCoB robustness for the
located on the fan-out area eWLB technology were listed and rated.
of the package are not The UBM, RDL and solder fatigue modes
very effective in lateral were analyzed using thermomechanical
heat transfer on account finite element simulation. The results show
Figure 8: A plot of phase shift vs. fatigue for single fatigue modes (RDL, of the long distance from that the driving forces of both UBM fatigue
UBM and solder ball fatigue), for RDL + UBM-fatigue, and for RDL + UBM + the silicon chip to the and RDL fatigue reduce with increasing
solder-ball-fatigue. solder balls and the limited level of fatigue and do not cause an end-of-
the phase shift may exceed the specification
limit (the gray area in Figure 8). The case
of more than 90% fatigue (e.g., 100%)
does not need to be considered because
100% will cause an electrical DC open.
Reliability testing for an electrical DC open
is done by standard TCoB testing, which
needs to fulfill the customer-specific TCoB
requirement anyway.
In summary, possible phase shifts of the
specified limit have to be applied to the
tolerances by setting up the system. The RF
ports, however, are not located at critical
TCoB positions such as package or die
corners, and therefore, have significantly
less than 90% fatigue. This is why the phase
Figure 9: Contribution of each solder ball to the overall heat dissipation for a typical eWLB radar package.
12
12 Chip Scale Review January • February • 2020 [ChipScaleReview.com]