Page 18 - Chip Scale Review_May June_2021-digital
P. 18
Moore’s Law and the future of test
By Pooya Tadayon, Greg Iovino, Sameer Ruiwale [Intel Corporation]
M oore’s Law – wh ich thought given that, at a per transistor and the test industry. Addressing these
h a s f u e l e d t h e
semiconductor industry level, it was several orders of magnitude challenges in an economically viable
manner is key to advancing Moore’s
less than the cost to manufacture a
for the last fifty years – is generally transistor. As late as 1997, however, the Law and will require a high degree of
associated with the observation that International Technology Roadmap for innovation and collaboration from players
the number of transistors on a chip Semiconductors (ITRS) highlighted that across the industry.
doubles at a regular cadence. As test cost per transistor was holding flat Die disaggregation and heterogeneous
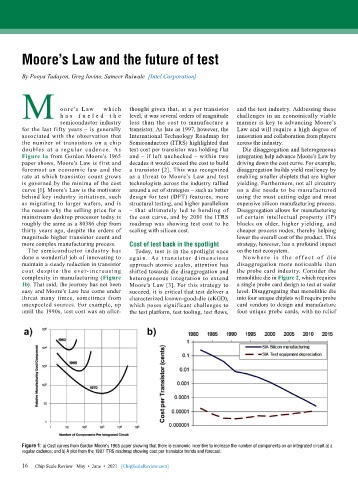
Figure 1a from Gordon Moore’s 1965 and – if left unchecked – within two integration help advance Moore’s Law by
paper shows, Moore’s Law is first and decades it would exceed the cost to build driving down the cost curve. For example,
foremost an economic law and the a transistor [2]. This was recognized disaggregation builds yield resiliency by
rate at which transistor count grows as a threat to Moore’s Law and test enabling smaller chiplets that are higher
is governed by the minima of the cost technologists across the industry rallied yielding. Furthermore, not all circuitry
curve [1]. Moore’s Law is the motivator around a set of strategies – such as better on a die needs to be manufactured
behind key industry initiatives, such design for test (DFT) features, more using the most cutting edge and most
as migrating to larger wafers, and is structural testing, and higher parallelism expensive silicon manufacturing process.
the reason why the selling price for a – that ultimately led to bending of Disaggregation allows for manufacturing
mainstream desktop processor today is the cost curve, and by 2001 the ITRS of certain intellectual property (IP)
roughly the same as a 80386 chip from roadmap was showing test cost to be blocks on older, higher yielding, and
thirty years ago, despite the orders of scaling with silicon cost. cheaper process nodes, thereby helping
magnitude higher transistor count and lower the overall cost of the product. This
more complex manufacturing process. Cost of test back in the spotlight strategy, however, has a profound impact
The semiconductor industry has Today, test is in the spotlight once on the test ecosystem.
done a wonderful job of innovating to agai n. As t ra nsistor d i mensions N o w h e r e i s t h e e f f e c t of d i e
maintain a steady reduction in transistor approach atomic scales, attention has disaggregation more noticeable than
cost despite t he ever-i ncreasi ng shifted towards die disaggregation and the probe card industry. Consider the
complexity in manufacturing (Figure heterogeneous integration to extend monolithic die in Figure 2, which requires
1b). That said, the journey has not been Moore’s Law [3]. For this strategy to a single probe card design to test at wafer
easy and Moore’s Law has come under succeed, it is critical that test deliver a level. Disaggregating that monolithic die
threat many times, sometimes from characterized known-good-die (cKGD), into four unique chiplets will require probe
unexpected sources. For example, up which poses significant challenges to card vendors to design and manufacture
until the 1990s, test cost was an after- the test platform, test tooling, test flows, four unique probe cards, with no relief
Figure 1: a) Cost curves from Gordon Moore’s 1965 paper showing that there is economic incentive to increase the number of components on an integrated circuit at a
regular cadence; and b) A plot from the 1997 ITRS roadmap showing cost per transistor trends and forecast.
16
16 Chip Scale Review May • June • 2021 [ChipScaleReview.com]