Page 19 - Chip Scale Review_May June_2021-digital
P. 19
driving the need for loopback-based test
methods in wafer test. These differences
between wafer test and package test can
result in higher yield loss downstream
and the cost-benefit tradeoff of such
approaches needs to be carefully
considered when architecting the product
and the manufacturing flow.
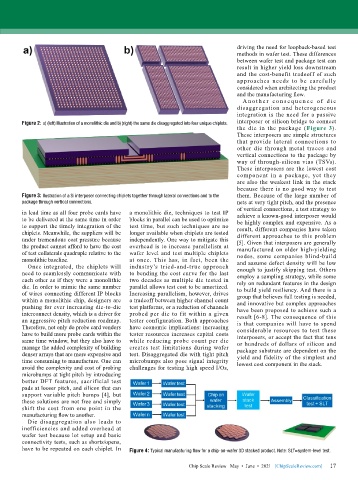
A n o t h e r c o n s e q u e n c e o f d i e
disaggregation and heterogeneous
integration is the need for a passive
Figure 2: a) (left) Illustration of a monolithic die and b) (right) the same die disaggregated into four unique chiplets. interposer or silicon bridge to connect
the die in the package (Figure 3).
These interposers are simple structures
that provide lateral connections to
other die through metal traces and
vertical connections to the package by
way of through-silicon vias (TSVs).
These interposers are the lowest cost
component in a package, yet they
are also the weakest link in the stack
because there is no good way to test
Figure 3: llustration of a Si interposer connecting chiplets together through lateral connections and to the them. Because of the large number of
package through vertical connections. nets at very tight pitch, and the presence
of vertical connections, a test strategy to
in lead time as all four probe cards have a monolithic die, techniques to test IP achieve a known-good interposer would
to be delivered at the same time in order blocks in parallel can be used to optimize be highly complex and expensive. As a
to support the timely integration of the test time, but such techniques are no result, different companies have taken
chiplets. Meanwhile, the suppliers will be longer available when chiplets are tested different approaches to this problem
under tremendous cost pressure because independently. One way to mitigate this [5]. Given that interposers are generally
the product cannot afford to have the cost overhead is to increase parallelism at manufactured on older high-yielding
of test collaterals quadruple relative to the wafer level and test multiple chiplets nodes, some companies blind-build
monolithic baseline. at once. This has, in fact, been the and assume defect density will be low
Once integrated, the chiplets will industry’s tried-and-true approach enough to justify skipping test. Others
need to seamlessly communicate with to bending the cost curve for the last employ a sampling strategy, while some
each other as if they were a monolithic two decades as multiple die tested in rely on redundant features in the design
die. In order to mimic the same number parallel allows test cost to be amortized. to build yield resiliency. And there is a
of wires connecting different IP blocks Increasing parallelism, however, drives group that believes full testing is needed,
within a monolithic chip, designers are a tradeoff between higher channel count and innovative but complex approaches
pushing for ever increasing die-to-die test platforms, or a reduction of channels have been proposed to achieve such a
interconnect density, which is a driver for probed per die to fit within a given result [6-8]. The consequence of this
an aggressive pitch reduction roadmap. tester configuration. Both approaches is that companies will have to spend
Therefore, not only do probe card vendors have economic implications: increasing considerable resources to test these
have to build more probe cards within the tester resources increases capital costs interposers, or accept the fact that tens
same time window, but they also have to while reducing probe count per die or hundreds of dollars of silicon and
manage the added complexity of building creates test limitations during wafer package substrate are dependent on the
denser arrays that are more expensive and test. Disaggregated die with tight pitch yield and fidelity of the simplest and
time consuming to manufacture. One can microbumps also pose signal integrity lowest cost component in the stack.
avoid the complexity and cost of probing challenges for testing high speed I/Os,
microbumps at tight pitch by introducing
better DFT features, sacrificial test
pads at looser pitch, and silicon that can
support variable pitch bumps [4], but
these solutions are not free and simply
shift the cost from one point in the
manufacturing flow to another.
Die disaggregation also leads to
inefficiencies and added overhead at
wafer test because lot setup and basic
connectivity tests, such as shorts/opens,
have to be repeated on each chiplet. In Figure 4: Typical manufacturing flow for a chip-on-wafer 3D stacked product. Note: SLT=system-level test.
17
Chip Scale Review May • June • 2021 [ChipScaleReview.com] 17