Page 50 - ChipScale_Mar-Apr_2021-digital
P. 50
Silicon die bonding using a photostructurable
adhesive material
By Kai Hollstein, Kirsten Weide-Zaage [Institute for Microelectronic Systems, RESRI Workgroup]
T his article addresses the commonly applied in order to build lithographically-structured SU-8 on
usage of a photostructurable
a d h e s i v e m a t e r i a l f o r microchannel systems. The following top. The resist has a thickness of 30µm
literature provides an overview with
and a minimum structure size of 5µm.
bonding a silicon chip onto a wafer respect to thin adhesive layers used in The paper addresses the inf luence
s u r fa c e. Such a p ro c e s s st e p i s wafer-to-wafer or substrate-to-wafer of pressure and bonding time on the
needed for a packaging technology bonding applications. bond quality, which is evaluated
currently under development. The I n [ 1 ] , a ph o t o s e n s i t i v e using microscopy and pull tests.
process under analysis demands that benzocyclobutene dielectric (BCB) Furthermore, the authors showed that
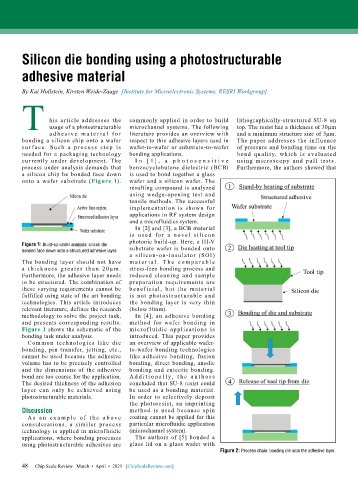
a silicon chip be bonded face down is used to bond together a glass
onto a wafer substrate (Figure 1). wafer and a silicon wafer. The
resulting compound is analyzed
using wedge-opening test and
tensile methods. The successful
implementation is shown for
applications in RF system design
and a microfluidics system.
In [2] and [3], a BCB material
i s u s e d fo r a n ovel si l ic o n
photonic build-up. Here, a III-V
Figure 1: Build-up under analysis: silicon die substrate wafer is bonded onto
bonded face down onto a structured adhesive layer.
a silicon-on-insulator (SOI)
The bonding layer should not have m a t e r i a l. T h e c o m p a r a b l e
a t h ick ne s s g r e at e r t h a n 20 µ m . stress-free bonding process and
Furthermore, the adhesive layer needs reduced cleaning and sample
to be structured. The combination of preparation requirements are
these varying requirements cannot be benef icial, but t he mater ial
fulfilled using state of the art bonding is not photostr ucturable and
technologies. This article introduces the bonding layer is very thin
relevant literature, defines the research (below 50nm).
methodology to solve the project task, In [4], an adhesive bonding
and presents corresponding results. method for wafer bonding in
Figure 1 shows the schematic of the microf luidic applications is
bonding task under analysis. introduced. This paper provides
Com mon tech nologies li ke die an overview of applicable wafer-
bonding, pin transfer, jetting, etc., to-wafer bonding technologies
cannot be used because the adhesive like adhesive bonding, fusion
volume has to be precisely controlled bonding, direct bonding, anodic
and the dimensions of the adhesive bonding and eutectic bonding.
bond are too coarse for the application. A d d i t i o n a l l y, t h e a u t ho r s
The desired thickness of the adhesion concluded that SU-8 resist could
layer can only be achieved using be used as a bonding material.
photostructurable materials. In order to selectively deposit
the photoresist, an imprinting
Discussion method is used because spin
A s a n e x a m p l e o f t h e a b o v e coating cannot be applied for this
considerations, a similar process particular microfluidic application
technology is applied in microfluidic (microchannel system).
applications, where bonding processes The authors of [5] bonded a
using photostructurable adhesives are glass lid on a glass wafer with
Figure 2: Process chain: bonding die onto the adhesive layer.
48 Chip Scale Review March • April • 2021 [ChipScaleReview.com]
48