Page 36 - ChipScale_Jan-Feb_2021-digital
P. 36
Extreme Si thinning and nano-TSVs to advance 3D
heterogeneous integration
By Dave Thomas [SPTS Technologies] Anne Jourdain [imec]
I t is anticipated that most of
the 3D system on chip (SoC)
integration schemes for the
future will require wafer-to-wafer
(W2W) bonding, which directly joins
the back-end-of-line (BEOL) layers of
two wafers, in combination with via-last
through-silicon via (TSV) connections.
This article presents a new approach
that combines extreme thinning of
silicon to a final thickness of 500nm,
together with subsequent etching of
nano-scale TSVs at sub-500nm pitch.
This allows for very high-density
electrical connections between the back
side and front side of a device wafer
as part of the back-side power delivery
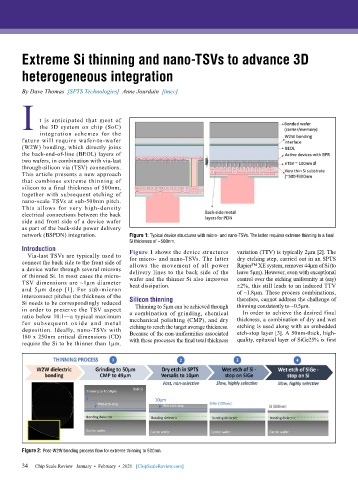
network (BSPDN) integration. Figure 1: Typical device structures with micro- and nano-TSVs. The latter requires extreme thinning to a final
Si thickness of ~500nm.
Introduction Figure 1 shows the device structures variation (TTV) is typically 2µm [2]. The
Via-last TSVs are typically used to for micro- and nano-TSVs. The latter dry etching step, carried out in an SPTS
connect the back side to the front side of allows the movement of all power Rapier™ XE system, removes 44µm of Si (to
a device wafer through several microns delivery lines to the back side of the leave 5µm). However, even with exceptional
of thinned Si. In most cases the micro- wafer and the thinner Si also improves control over the etching uniformity at (say)
TSV dimensions are ~1µm diameter heat dissipation. ±2%, this still leads to an induced TTV
and 5µm deep [1]. For sub-micron of ~1.8µm. These process combinations,
interconnect pitches the thickness of the therefore, cannot address the challenge of
Si needs to be correspondingly reduced Silicon thinning thinning consistently to ~0.5µm.
in order to preserve the TSV aspect Thinning to 5µm can be achieved through In order to achieve the desired final
ratio below 10:1—a typical maximum a combination of grinding, chemical thickness, a combination of dry and wet
for subse que nt ox ide a nd met al mechanical polishing (CMP), and dry etching is used along with an embedded
deposition. Ideally, nano-TSVs with etching to reach the target average thickness. etch-stop layer [3]. A 50nm-thick, high-
180 x 250nm critical dimensions (CD) Because of the non-uniformities associated quality, epitaxial layer of SiGe25% is first
require the Si to be thinner than 1µm. with these processes the final total thickness
Figure 2: Post-W2W bonding process flow for extreme thinning to 500nm.
34 Chip Scale Review January • February • 2021 [ChipScaleReview.com]
34