Page 23 - ChipScale_Jan-Feb_2021-digital
P. 23
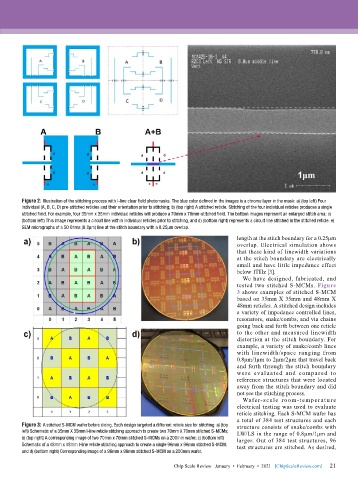
Figure 2: Illustration of the stitching process with I-line clear field photomasks. The blue color defined in the images is a chrome layer in the mask: a) (top left) Four
individual (A, B, C, D) pre-stitched reticles and their orientation prior to stitching; b) (top right) A stitched reticle. Stitching of the four individual reticles produces a single
stitched field. For example, four 35mm x 35mm individual reticles will produce a 70mm x 70mm-stitched field. The bottom images represent an enlarged stitch area: c)
(bottom left) This image represents a circuit line within individual reticles prior to stitching, and d) (bottom right) represents a circuit line stitched in the stitched reticle. e)
SEM micrographs of a 50 Ohms (0.8μm) line at the stitch boundary with a 0.25μm overlap.
length at the stitch boundary for a 0.25μm
overlap. Electrical simulation shows
that these kind of linewidth variations
at the stitch boundary are electrically
small and have little impedance effect
below 1THz [3].
We have designed, fabricated, and
tested two stitched S-MCMs. Figure
3 shows examples of stitched S-MCM
based on 35mm X 35mm and 48mm X
48mm reticles. A stitched design includes
a variety of impedance controlled lines,
resonators, snake/combs, and via chains
going back and forth between one reticle
to the other and measured linewidth
distortion at the stitch boundary. For
example, a variety of snake/comb lines
with linewidth/space ranging from
0.8μm/1μm to 2μm/2μm that travel back
and forth through the stitch boundary
were evaluated and compared to
reference structures that were located
away from the stitch boundary and did
not see the stitching process.
Wafer-scale room-temperat u re
electrical testing was used to evaluate
reticle stitching. Each S-MCM wafer has
a total of 384 test structures and each
Figure 3: A stitched S-MCM wafer before dicing. Each design targeted a different reticle size for stitching: a) (top structure consists of snake/combs with
left) Schematic of a 35mm X 35mm I-line reticle stitching approach to create two 70mm X 70mm stitched S-MCMs; LW/LS in the range of 0.8μm/1μm and
b) (top right) A corresponding image of two 70mm x 70mm stitched S-MCMs on a 200mm wafer; c) (bottom left) larger. Out of 384 test structures, 96
Schematic of a 48mm x 48mm I-line reticle stitching approach to create a single 96mm x 96mm stitched S-MCM; test structures are stitched. As desired,
and d) (bottom right) Corresponding image of a 96mm x 96mm stitched S-MCM on a 200mm wafer.
21
Chip Scale Review January • February • 2021 [ChipScaleReview.com] 21