Page 28 - ChipScale_Jul-Aug_2020-Digital
P. 28
Achieving less than 1% voiding in GaN die
attach processing
By Alex Voronel, Pierino (Zap) Zappela [SST Vacuum Reflow Systems, a Palomar Solution]
T he die bonding, or die attach the AuSn can be used as a die attach, as There are essential metallization
process, consists of attaching
a die/chip to a substrate well as a lid seal, on the same package. considerations that must be followed to
enable proper solder wetting. There are
The reflowed die-attach solder will require
or package. This attachment can be a higher melting point and, therefore, will different types of gold plating baths for
performed with either eutectic solder or remain solid for the lid seal reflow process various applications. Gold brighteners
adhesive (epoxy). This article will discuss used to attach the lid. (metallic or organic additives) — often
the eutectic (where the liquidus and All materials used in the assembly incorporated for bright shiny gold
solidus temperature are the same) solder of electronic components must be appearance (typically used for jewelry) —
die attach where the preform is an alloy considered as an integral part of the do not promote good solder wetting and
comprising a mixture of two or more overall design. In particular, the selection can result in poor adhesion. When used,
dissimilar metals. The preform is a flat of the preform material is paramount gold brighteners are often responsible
sheet of material slightly smaller in area for hermetic leak
than the die. This preform is typically failures for lid seal
25–50µm thick. It is placed between the a p p l i c a t i o n s . I t
die and substrate for subsequent melting is re com mended
to wet both the backside of the gold- t hat t he gold be
coated die, and the gold surface of the underplated with
package/substrate. In our evaluation, the a (1. 27–3.81µ m)
AuSn preform was used with the exact t h ic k l a y e r o f
ratio of 80% gold and 20% tin with a solderable nickel
melting point of 278°C. This is a critical sulfamate per QC-
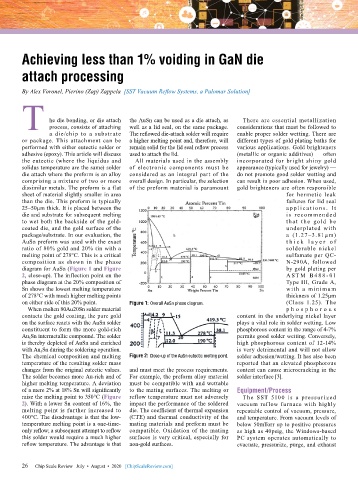
composition as shown in the phase N-290A, followed
diagram for AuSn (Figure 1 and Figure by gold plating per
2, close-up). The inflection point on the A S T M B 48 8 - 01
phase diagram at the 20% composition of Type III, Grade A,
Sn shows the lowest melting temperature with a minimu m
of 278°C with much higher melting points thickness of 1.25µm
on either side of this 20% point. Figure 1: Overall AuSn phase diagram. (Class 1.25). The
When molten 80Au20Sn solder material ph o s ph o r ou s
contacts the gold coating, the pure gold content in the underlying nickel layer
on the surface reacts with the AuSn solder plays a vital role in solder wetting. Low
constituent to form the more gold-rich phosphorous content in the range of 4-7%
Au 5 Sn intermetallic compound. The solder permits good solder wetting. Conversely,
is thereby depleted of AuSn and enriched high phosphorous content of 12-14%
with Au 5 Sn during the soldering operation. is very detrimental and will not allow
The chemical composition and melting Figure 2: Close-up of the AuSn eutectic melting point. solder adhesion/wetting. It has also been
temperature of the resulting solder mass reported that an elevated phosphorous
changes from the original eutectic values. and must meet the process requirements. content can cause microcracking in the
The solder becomes more Au-rich and of For example, the preform alloy material solder interface [3].
higher melting temperature. A deviation must be compatible with and wettable
of a mere 2% at 18% Sn will significantly to the mating surfaces. The melting or Equipment/Process
raise the melting point to 350°C (Figure reflow temperature must not adversely The SST 5100 is a pressur ized
2). With a lower Sn content of 16%, the impact the performance of the soldered vacuum reflow furnace with highly
melting point is further increased to die. The coefficient of thermal expansion repeatable control of vacuum, pressure,
400°C. The disadvantage is that the low- (CTE) and thermal conductivity of the and temperature. From vacuum levels of
temperature melting point is a one-time- mating materials and preform must be below 50mTorr up to positive pressures
only reflow; a subsequent attempt to reflow compatible. Oxidation of the mating as high as 40psig, the Windows-based
this solder would require a much higher surfaces is very critical, especially for PC system operates automatically to
reflow temperature. The advantage is that non-gold surfaces. evacuate, pressurize, purge, and exhaust
26 Chip Scale Review July • August • 2020 [ChipScaleReview.com]
26