Page 24 - ChipScale_Jul-Aug_2020-Digital
P. 24
Solder stock is supplied in three main
forms: paste, preform (freeform/pre-
applied on substrate/die backside), and
wire. Solder paste is most commonly
deployed by means of a stencil-printing
process. The solder paste must be tacky
enough to secure the components in
place throughout the production process,
especially until the reflow process.
During the ref low process, tight
control of the temperature profiles is
extremely important. The temperature
rate of increase must be slow enough to
prevent solder balling, while also being
fast enough not to deplete the flux. The
ultimate temperature needs to be as
low as possible to avoid damage, but
still high enough to fully activate the
flux, melt the solder itself, and allow
for adequate wetting. Cooling should
be quick enough to retain the desired
shape and prevent oxidation, while slow
enough to control substrate warpage.
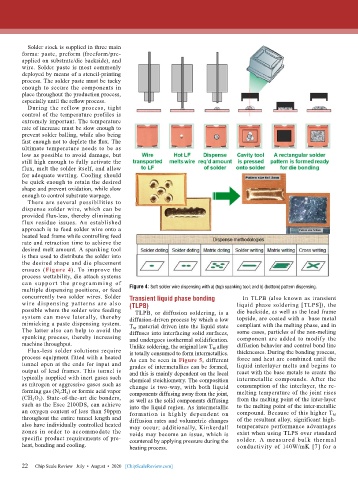
There are several possibilities to
dispense solder wire, which can be
provided flux-less, thereby eliminating
f lux residue issues. An established
approach is to feed solder wire onto a
heated lead frame while controlling feed
rate and retraction time to achieve the
desired melt amount. A spanking tool
is then used to distribute the solder into
the desired shape and die placement
ensues (Figure 4). To improve the
process wettability, die attach systems
can suppor t the prog ram ming of
multiple dispensing positions, or feed Figure 4: Soft solder wire dispensing with a) (top) spanking tool; and b) (bottom) pattern dispensing.
concurrently two solder wires. Solder Transient liquid phase bonding In TLPB (also known as transient
wire dispensing patterns are also (TLPB) liquid phase soldering [TLPS]), the
possible where the solder wire feeding TLPB, or diffusion soldering, is a die backside, as well as the lead frame
system can move laterally, thereby diffusion-driven process by which a low topside, are coated with a base metal
mimicking a paste dispensing system. T M material driven into the liquid state compliant with the melting phase, and in
The latter also can help to avoid the diffuses into interfacing solid surfaces, some cases, particles of the non-melting
spanking process, thereby increasing and undergoes isothermal solidification. component are added to modify the
machine throughput. Unlike soldering, the original low T M alloy diffusion behavior and control bond line
Flux-less solder solutions require is totally consumed to form intermetallics. thicknesses. During the bonding process,
process equipment fitted with a heated As can be seen in Figure 5, different force and heat are combined until the
tunnel open at the ends for input and grades of intermetallics can be formed, liquid interlayer melts and begins to
output of lead frames. This tunnel is and this is mainly dependent on the local react with the base metals to create the
typically supplied with inert gases such chemical stoichiometry. The composition intermetallic compounds. After the
as nitrogen or aggressive gases such as change is two-way, with both liquid consumption of the interlayer, the re-
forming gas (N 2 :H 2 ) or formic acid vapor components diffusing away from the joint, melting temperature of the joint rises
(CH 2 O 2 ). State-of-the-art die bonders, as well as the solid components diffusing from the melting point of the inter-layer
such as the Esec 2100DS, can achieve into the liquid region. As intermetallic to the melting point of the inter-metallic
an oxygen content of less than 50ppm formation is highly dependent on compound. Because of this higher T M
throughout the entire tunnel length and diffusion rates and volumetric changes of the resultant alloy, significant high-
also have individually controlled heated may occur; additionally, Kinkerdall temperature performance advantages
zones in order to accommodate the voids may become an issue, which is exist when using TLPS over standard
specific product requirements of pre- countered by applying pressure during the solder. A measured bulk ther mal
heat, bonding and cooling. heating process. conductivity of 140W/mK [7] for a
22 Chip Scale Review July • August • 2020 [ChipScaleReview.com]
22