Page 30 - Chip Scale Review_January-February_2024-digital
P. 30
Bridges maturity levels can often influence the layout early in the design flow process
The next iteration of HDFO enables decision making of our customers. can significantly facilitate a smooth
a 3D capability using bridge silicon Our version (S-Connect) of the supply chain support path. Notably, this
and other embedded components under embedded bridge HDFO module on solution is compatible with multiple
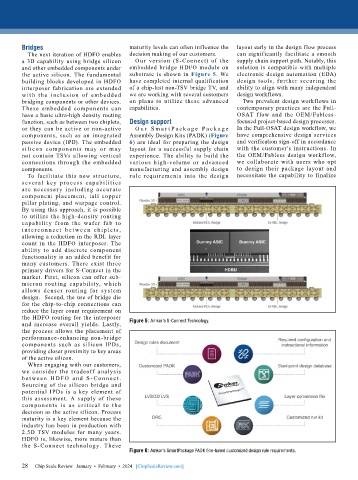
the active silicon. The fundamental substrate is shown in Figure 5. We electronic design automation (EDA)
building blocks developed in HDFO have completed internal qualification design tools, further securing the
interposer fabrication are extended of a chip-last non-TSV bridge TV, and ability to align with many independent
w it h t he i nclu sion of embedded we are working with several customers design workflows.
bridging components or other devices. on plans to utilize these advanced Two prevalent design workflows in
These embedded components can capabilities. contemporary practices are the Full-
have a basic ultra-high density routing OSAT f low and the OEM/Fabless-
function, such as between two chiplets, Design support focused project-based design processes.
or they can be active or non-active O u r Sm a r t P a c k a g e P a c k a g e In the Full-OSAT design workflow, we
components, such as an integrated Assembly Design Kits (PADK) (Figure have comprehensive design services
passive device (IPD). The embedded 6) are ideal for preparing the design and verification sign-off in accordance
sil icon component s may or may layout for a successful supply chain with the customer’s instructions. In
not contain TSVs allowing vertical experience. The ability to build the the OEM/Fabless design workf low,
connections through the embedded various high-volume or advanced we collaborate with users who opt
components. manufacturing and assembly design to design their package layout and
To facilitate this new structure, rule requirements into the design necessitate the capability to finalize
several key process capabilit ies
are necessar y including accurate
component placement, tall copper
pillar plating, and warpage control.
By using this approach, it is possible
to utilize the high-density routing
capabilit y f rom the wafer fab to
i n ter c o n n ec t b e t we e n c h i ple t s ,
allowing a reduction in the RDL layer
count in the HDFO interposer. The
ability to add discrete component
functionality is an added benefit for
many customers. There exist three
primary drivers for S-Connect in the
market. First, silicon can offer sub-
micron routing capability, which
allows denser routing for system
design. Second, the use of bridge die
for the chip-to-chip connections can
reduce the layer count requirement on
the HDFO routing for the interposer
and increase overall yields. Lastly, Figure 5: Amkor’s S-Connect Technology.
the process allows the placement of
performance-enhancing non-bridge
components such as silicon IPDs,
providing closer proximity to key areas
of the active silicon.
When engaging with our customers,
we consider the tradeoff analysis
b e t we e n H DFO a nd S - C o n ne c t .
Sourcing of the silicon bridge and
potential IPDs is a key element of
this assessment. A supply of these
components is as cr it ical to t he
decision as the active silicon. Process
maturity is a key element because the
industry has been in production with
2.5D TSV modules for many years.
HDFO is, likewise, more mature than
the S-Connect technology. These
Figure 6: Amkor’s SmartPackage PADK fine-tuned customized design rule requirements.
28
28 Chip Scale Review January • February • 2024 [ChipScaleReview.com]