Page 28 - Chip Scale Review_January-February_2024-digital
P. 28
HDFO
Modules based on HDFO interposers
have been internally qualified and
several of our customers’ products
are in qualification. Our internal
terminology for HDFO is S-SWIFT
(Substrate Silicon Wafer Integrated
F a n - o u t Te c h n o log y ) . H D F O
technology is being applied to many
markets and use applications, ranging
f rom high-per for mance compute
and AI, to automotive applications
and beyond. Chiplet architectures
are leading to a push for advanced
pack ag i ng desig n r u les t hat a re
enabled by HDFO and other module-
based solutions. Our fabrication of
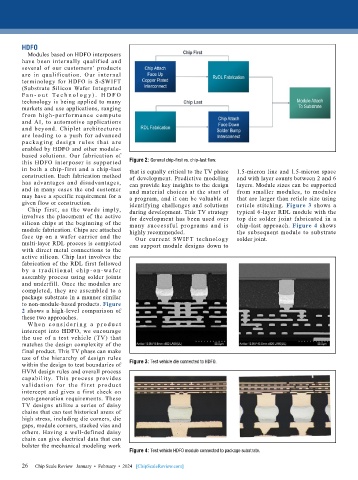
this HDFO interposer is supported Figure 2: General chip-first vs. chip-last flow.
in both a chip-first and a chip-last that is equally critical to the TV phase 1.5-micron line and 1.5-micron space
construction. Each fabrication method of development. Predictive modeling and with layer counts between 2 and 6
has advantages and disadvantages, can provide key insights to the design layers. Module sizes can be supported
and in many cases the end customer and material choices at the start of from smaller modules, to modules
may have a specific requirement for a a program, and it can be valuable at that are larger than reticle size using
given flow or construction. identifying challenges and solutions reticle stitching. Figure 3 shows a
Chip f irst, as the words imply, during development. This TV strategy typical 6-layer RDL module with the
involves the placement of the active for development has been used over top die solder joint fabricated in a
silicon chips at the beginning of the many successful programs and is chip-last approach. Figure 4 shows
module fabrication. Chips are attached highly recommended. the subsequent module to substrate
face up on a wafer carrier and the Our cur rent SWIFT technology solder joint.
multi-layer RDL process is completed can support module designs down to
with direct metal connections to the
active silicon. Chip last involves the
fabrication of the RDL first followed
b y a t r a d i t i o n a l c h i p - o n -wa fe r
assembly process using solder joints
and underfill. Once the modules are
completed, they are assembled to a
package substrate in a manner similar
to non-module-based products. Figure
2 shows a high-level comparison of
these two approaches.
W h e n c o n s i d e r i n g a p r o d u c t
intercept into HDFO, we encourage
the use of a test vehicle (TV) that
matches the design complexity of the
final product. This TV phase can make
use of the hierarchy of design rules
within the design to test boundaries of Figure 3: Test vehicle die connected to HDFO.
HVM design rules and overall process
capability. This process provides
va l id at ion for t he f i r st pro d uc t
intercept and gives a first check on
next-generation requirements. These
TV designs utilize a series of daisy
chains that can test historical areas of
high stress, including die corners, die
gaps, module corners, stacked vias and
others. Having a well-defined daisy
chain can give electrical data that can
bolster the mechanical modeling work
Figure 4: Test vehicle HDFO module connected to package substrate.
26
26 Chip Scale Review January • February • 2024 [ChipScaleReview.com]