Page 39 - Chip Scale Review_September-October_2023-digital
P. 39
Efficiency and cost implications of multi-die
heterogeneous integration
By Glenn Farris [Universal Instruments]
T he semiconductor industry is actively working
towards achieving widespread integration of
diverse semiconductor die types through a
technique known as heterogeneous integration (HI). These die
can originate from various wafer sizes and are produced using
different technological processes. This emerging packaging
method presents fresh challenges related to the efficiency of
assembly and the overall yield.
Historically, the process of flip-chip assembly has employed
a single tool to position a singular die type onto the intended
substrate. In cases involving multiple die types, manufacturing
lines have been configured with a sequence of placement
tools, each designated for a specific die type. This article
delves into the implications of such an approach in the context
of the HI era. The effects on product yield, production
speed, manufacturing efficiency, and the comprehensive
cost of assembly are investigated across a wide array of HI
die setups.
An innovative strategy is proposed for optimizing the
comprehensive economic aspects of the assembly. This
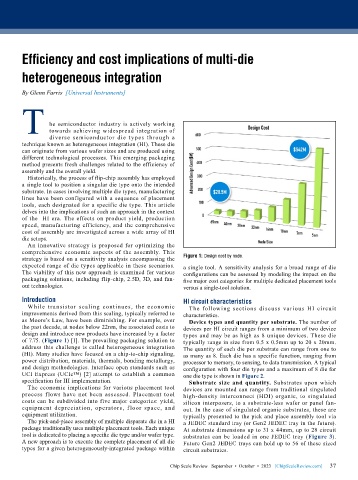
strategy is based on a sensitivity analysis encompassing the Figure 1: Design cost by node.
expected range of die types applicable in these scenarios. a single tool. A sensitivity analysis for a broad range of die
The viability of this new approach is examined for various configurations can be assessed by modeling the impact on the
packaging solutions, including flip-chip, 2.5D, 3D, and fan- five major cost categories for multiple dedicated placement tools
out technologies. versus a single-tool solution.
Introduction HI circuit characteristics
While transistor scaling continues, the economic The following sections discuss various HI circuit
improvements derived from this scaling, typically referred to characteristics.
as Moore’s Law, have been diminishing. For example, over Device types and quantity per substrate. The number of
the past decade, at nodes below 22nm, the associated costs to devices per HI circuit ranges from a minimum of two device
design and introduce new products have increased by a factor types and may be as high as 8 unique devices. These die
of 7.75. (Figure 1) [1]. The prevailing packaging solution to typically range in size from 0.5 x 0.5mm up to 20 x 20mm.
address this challenge is called heterogeneous integration The quantity of each die per substrate can range from one to
(HI). Many studies have focused on a chip-to-chip signaling, as many as 8. Each die has a specific function, ranging from
power distribution, materials, thermals, bonding metallurgy, processor to memory, to sensing, to data transmission. A typical
and design methodologies. Interface open standards such as configuration with four die types and a maximum of 8 die for
UCI Express (UCIe™) [2] attempt to establish a common one die type is shown in Figure 2.
specification for HI implementation. Substrate size and quantity. Substrates upon which
The economic implications for various placement tool devices are mounted can range from traditional singulated
process f lows have not been assessed. Placement tool high-density interconnect (HDI) organic, to singulated
costs can be subdivided into five major categories: yield, silicon interposers, to a substrate-less wafer or panel fan-
equipment depreciation, operators, f loor space, and out. In the case of singulated organic substrates, these are
equipment utilization. typically presented to the pick and place assembly tool via
The pick-and-place assembly of multiple disparate die in a HI a JEDEC standard tray (or Gen2 JEDEC tray in the future).
package traditionally uses multiple placement tools. Each unique At substrate dimensions up to 31 x 44mm, up to 28 circuit
tool is dedicated to placing a specific die type and/or wafer type. substrates can be loaded in one JEDEC tray (Figure 3).
A new approach is to execute the complete placement of all die Future Gen2 JEDEC trays can hold up to 56 of these sized
types for a given heterogeneously-integrated package within circuit substrates.
37
Chip Scale Review September • October • 2023 [ChipScaleReview.com] 37