Page 40 - Chip Scale Review_January February_2023-digital
P. 40
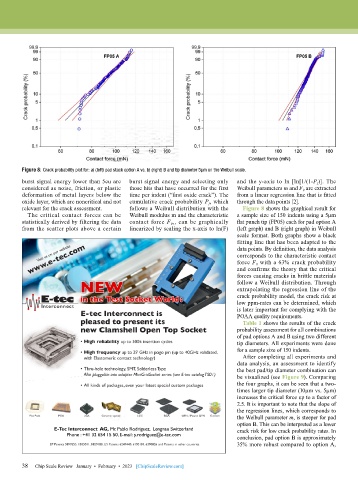
Figure 8: Crack probability plot for: a) (left) pad stack option A vs. b) (right) B and tip diameter 5µm on the Weibull scale.
burst signal energy lower than 5eu are burst signal energy and selecting only and the y-axis to ln [ln[1/(1-P f )]. The
considered as noise, friction, or plastic those hits that have occurred for the first Weibull parameters m and F 0 are extracted
deformation of metal layers below the time per indent (“first oxide crack”). The from a linear regression line that is fitted
oxide layer, which are noncritical and not cumulative crack probability P f , which through the data points [2].
relevant for the crack assessment. follows a Weibull distribution with the Figure 8 shows the graphical result for
The critical contact forces can be Weibull modulus m and the characteristic a sample size of 150 indents using a 5µm
statistically derived by filtering the data contact force F 0 ,, can be graphically flat punch tip (FP05) each for pad option A
from the scatter plots above a certain linearized by scaling the x-axis to ln(F) (left graph) and B (right graph) in Weibull
scale format. Both graphs show a black
fitting line that has been adapted to the
data points. By definition, the data analysis
corresponds to the characteristic contact
force F 0 with a 63% crack probability
and confirms the theory that the critical
forces causing cracks in brittle materials
follow a Weibull distribution. Through
extrapolating the regression line of the
crack probability model, the crack risk at
low ppm-rates can be determined, which
is later important for complying with the
POAA quality requirements.
Table 1 shows the results of the crack
probability assessment for all combinations
of pad options A and B using two different
tip diameters. All experiments were done
for a sample size of 150 indents.
After completing all experiments and
data analysis, an assessment to identify
the best pad/tip diameter combination can
be visualized (see Figure 9). Comparing
the four graphs, it can be seen that a two-
times larger tip diameter (10µm vs. 5µm)
increases the critical force up to a factor of
2.5. It is important to note that the slope of
the regression lines, which corresponds to
the Weibull parameter m, is steeper for pad
option B. This can be interpreted as a lower
E-Tec Interconnect AG, Mr. Pablo Rodriguez, Lengnau Switzerland crack risk for low crack probability rates. In
Phone : +41 32 654 15 50, E-mail: p.rodriguez@e-tec.com conclusion, pad option B is approximately
35% more robust compared to option A,
38
38 Chip Scale Review January • February • 2023 [ChipScaleReview.com]