Page 54 - Chip Scale Review Sep Oct_2022-digital
P. 54
widespread interconnection technology in the
electronics industry.
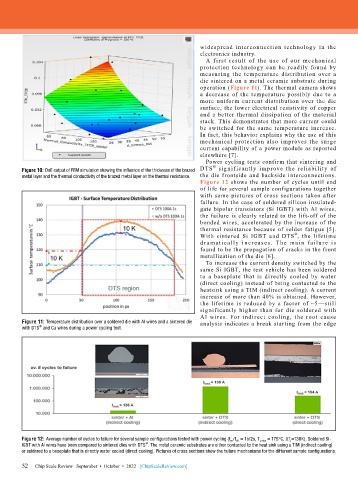
A f irst result of the use of our mechanical
protection technology can be readily found by
measuring the temperature distribution over a
die sintered on a metal ceramic substrate during
operation (Figure 11). The thermal camera shows
a decrease of the temperature possibly due to a
more uniform current distribution over the die
surface, the lower electrical resistivity of copper
and a better thermal dissipation of the material
stack. This demonstrates that more current could
be switched for the same temperature increase.
In fact, this behavior explains why the use of this
mechanical protection also improves the surge
current capability of a power module as reported
elsewhere [7].
Power cycling tests confirm that sintering and
®
Figure 10: DoE output of FEM simulation showing the influence of the thickness of the brazed DTS signif icantly improve the reliability of
metal layer and the thermal conductivity of the brazed metal layer on the thermal resistance. the die frontside and backside interconnections.
Figure 12 shows the number of cycles until end
of life for several sample configurations together
with some pictures of cross sections taken after
failure. In the case of soldered silicon insulated-
gate bipolar transistors (Si IGBT) with Al wires,
the failure is clearly related to the lift-off of the
bonded wires, accelerated by the increase of the
thermal resistance because of solder fatigue [5].
®
With sintered Si IGBT and DTS , the lifetime
d r a mat ically i ncreases. T he mai n failu re is
found to be the propagation of cracks in the front
metallization of the die [6].
To increase the current density switched by the
same Si IGBT, the test vehicle has been soldered
to a baseplate that is directly cooled by water
(direct cooling) instead of being contacted to the
heatsink using a TIM (indirect cooling). A current
increase of more than 40% is obtained. However,
the lifetime is reduced by a factor of ~5—still
significantly higher than for die soldered with
Al wires. For indirect cooling, the root cause
Figure 11: Temperature distribution over a soldered die with Al wires and a sintered die analysis indicates a break starting from the edge
®
with DTS and Cu wires during a power cycling test.
Figure 12: Average number of cycles to failure for several sample configurations tested with power cycling (t on /t off = 1s/2s, T j,max = 175°C, ΔT j =130K). Soldered Si-
®
IGBT with Al wires have been compared to sintered dies with DTS . The metal ceramic substrates are either contacted to the heat sink using a TIM (indirect cooling)
or soldered to a baseplate that is directly water cooled (direct cooling). Pictures of cross sections show the failure mechanisms for the different sample configurations.
52 Chip Scale Review September • October • 2022 [ChipScaleReview.com]
52