Page 19 - Chip Scale Review_Jul Aug_2022-digital
P. 19
When we look at the various package
platform roadmaps today, we see a trend
around miniaturization, not necessarily
just for final package size, but also for
performance. For the mobile space,
the original equipment manufacturer
(OEM) suppliers are driving component
size reduction or integration across
all sub-modules to enable more room
for new functionality while managing
battery space.
Table 1 by TSR in February 2022
shows the modular adoption rate
across various radio frequency (RF)
modules. The one reduced adoption
is partially due to the exit of LG,
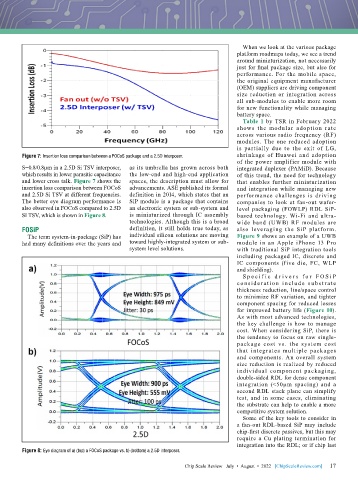
Figure 7: Insertion loss comparison between a FOCoS package and a 2.5D interposer. shrinkage of Huawei and adoption
of the power amplifier module with
S=0.8/0.8µm in a 2.5D Si TSV interposer, as its umbrella has grown across both integrated duplexer (PAMiD). Because
which results in lower parasitic capacitance the low-end and high-end application of this trend, the need for technology
and lower cross talk. Figure 7 shows the spaces, the description must allow for that enables further miniaturization
insertion loss comparison between FOCoS advancements. ASE published its formal and integration while managing new
and 2.5D Si TSV at different frequencies. definition in 2014, which states that an performance challenges is driving
The better eye diagram performance is SiP module is a package that contains companies to look at fan-out wafer-
also observed in FOCoS compared to 2.5D an electronic system or sub-system and level packaging (FOWLP) RDL SiP-
SI TSV, which is shown in Figure 8. is miniaturized through IC assembly based technology. Wi-Fi and ultra-
technologies. Although this is a broad wide band (UWB) RF modules are
FOSiP definition, it still holds true today, as also leveraging the SiP platform.
The term system-in-package (SiP) has individual silicon solutions are moving Figure 9 shows an example of a UWB
had many definitions over the years and toward highly-integrated system or sub- module in an Apple iPhone 13 Pro
system level solutions. with traditional SiP integration tools
including packaged IC, discrete and
IC components (five die, FC, WLP
and shielding).
S p e c i f i c d r i v e r s f o r F OS i P
c on side r at ion i nclude s ubst r at e
thickness reduction, line/space control
to minimize RF variation, and tighter
component spacing for reduced losses
for improved battery life (Figure 10).
As with most advanced technologies,
the key challenge is how to manage
cost. When considering SiP, there is
the tendency to focus on raw single-
package cost vs. the system cost
that integrates multiple packages
and components. An overall system
size reduction is realized by reduced
individual component packaging,
double-sided RDL for dense component
integration (<50µm spacing) and a
second RDL stack plane can simplify
test, and in some cases, eliminating
the substrate can help to enable a more
competitive system solution.
Some of the key tools to consider in
a fan-out RDL-based SiP may include
chip-first discrete passives, but this may
require a Cu plating termination for
integration into the RDL; or if chip last
Figure 8: Eye diagram of a) (top) a FOCoS package vs. b) (bottom) a 2.5D interposer.
17
Chip Scale Review July • August • 2022 [ChipScaleReview.com] 17