Page 20 - Chip Scale Review_March April_2022-digital
P. 20
FO-EB-T (where “T” represents through- i n wh ich t he d ies a re ver t ically layers of RDL with 2/2µm L/S, and
2
silicon via); in these structures, the top interconnected. It is generally used to the package size is 6,000mm , which
dies are connected by a silicon bridge connect the top low-power double data is covered by a lid-type heat sink
die and a RDL. The bridge die plays the rate (LPDDR) memory with the bottom on the top. Figure 2b shows that 6L
main role with respect to communicating system on chip (SoC) die. Therefore, the RDLs are built up with C4 bumps for
in the high-speed area between the die- small form factor, thin package height the vertical transmission of signal
to-die structure. Because of the fine- and low power consumption are the key and power from active dies to the
pitch and small L/S design, the metal design factors for FO-PoP. Finally, FO- substrate. The FO-MCM structure is
L/S on the bridge die is normally smaller MCM is another main platform that is highly flexible for advanced package
than 0.56µm. Therefore, compared to widely applied in advanced packaging. d e sig n i n t e r m s of t he C u w i r e
2.5D, FO-EB only requires a small In FO-MCM, the RDL connects the top inside the RDL layers. FO-MCM is,
silicon die size at the interconnect area, dies horizontally using multi-layers of therefore, also a robust platform for
which reduces the interposer cost by RDL; and the L/S is generally scalable both homogeneous and heterogeneous
reducing the gross die size and raising between 2/2µm~10/10µm. This flexible integration, owing to the advantages of
the yield performance for each interposer routing design is better for power and known-good RDL before die attaching
wafer. Furthermore, FO-EB-T (which is signal integrity. On the other hand, FO- and a competitive manufacturing cost.
designed using TSV structures) inside MCM is the ideal structure to achieve a Additionally, FO-MCM has a shorter
the bridge die is the next cutting-edge lower cost than 2.5D because the costly development cycle time than 2.5D and
packaging technology. Using a TSV silicon interposer is not required [6-9]. FO-EB because the RDL interposer
design in the FO-EB-T structure, the can be grown before the wafer arrives
electrical performance is enhanced by Fan-out multi-chip module (FO- at the outsourced assembly and test
shortening the signal or power delivery MCM) package technology (OSAT) site for chip-last processing.
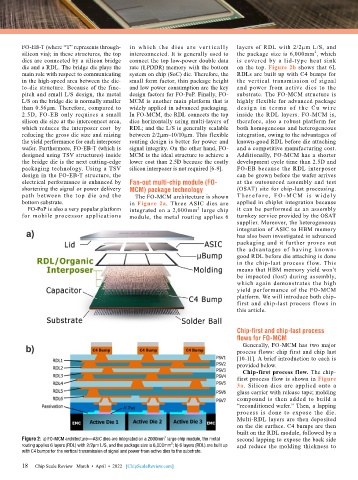
path between the top die and the The FO-MCM architecture is shown T h e r ef o r e , FO - M C M i s w i d el y
bottom substrate. in Figure 2a. Three ASIC dies are applied in chiplet integration because
FO-PoP is also a very popular platform integrated on a 2,000mm large chip it can be performed as an assembly
2
for mobile processor applications module, the metal routing applies 6 turnkey service provided by the OSAT
supplier. Moreover, the heterogeneous
integration of ASIC to HBM memory
has also been investigated in advanced
packaging and it further proves out
the advantages of having known-
good RDL before die attaching is done
in the chip-last process f low. This
means that HBM memory yield won’t
be impacted (lost) during assembly,
which again demonstrates the high
yield performance of the FO-MCM
platform. We will introduce both chip-
first and chip-last process flows in
this article.
Chip-first and chip-last process
flows for FO-MCM
Generally, FO-MCM has two major
process flows: chip first and chip last
[10-11]. A brief introduction to each is
provided below.
Chip-first process flow. The chip-
first process flow is shown in Figure
3a. Silicon dies are applied onto a
glass carrier with release tape; molding
compound is then added to build a
“reconditioned wafer.” Then, a lapping
process is done to expose the die.
Multi-RDL layers are then deposited
on the die surface. C4 bumps are then
built on the RDL module, followed by a
2
Figure 2: a) FO-MCM architecture—ASIC dies are integrated on a 2000mm large chip module, the metal second lapping to expose the back side
routing applies 6 layers (RDL) with 2/2µm L/S, and the package size is 6,000mm ; b) 6 layers (RDL) are built up and reduce the molding thickness to
2
with C4 bumps for the vertical transmission of signal and power from active dies to the substrate.
18
18 Chip Scale Review March • April • 2022 [ChipScaleReview.com]