Page 53 - Chip Scale Review_January February_2022-digital
P. 53
if necessary. It is used to prevent the
underfill in the subsequent step from
f lowing to the optical I/O area, or
protected area. The singulation process
is designed so that the PIC buffer area
together with its surrounding mold are
diced off at Step 7. The FOWLP of the
EIC and PIC with optical edge coupling
is then formed. The integrated photonics
FOWLP module can then be flip-chip
assembled to the main optical board or
substrate for the main integration. The
process described above is compatible
with the FOWLP process. IME is
currently developing the complete
process and evaluating the optical
coupling performance.
Figure 7a shows the PIC test vehicle
after the FOWLP molding process
before the dicing is done. The buffer
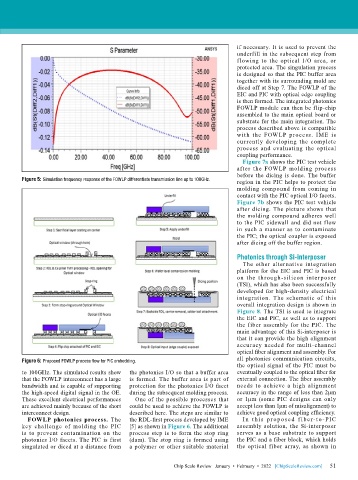
Figure 5: Simulation frequency response of the FOWLP differentiate transmission line up to 100GHz. region in the PIC helps to protect the
molding compound from coming in
contact with the PIC optical I/O facets.
Figure 7b shows the PIC test vehicle
after dicing. The picture shows that
the molding compound adheres well
to the PIC sidewall and did not flow
in such a manner as to contaminate
the PIC; the optical coupler is exposed
after dicing off the buffer region.
Photonics through Si-interposer
The other alternative integration
platform for the EIC and PIC is based
on the through-silicon inter poser
(TSI), which has also been successfully
developed for high-density electrical
integration. The schematic of this
overall integration design is shown in
Figure 8. The TSI is used to integrate
the EIC and PIC, as well as to support
the fiber assembly for the PIC. The
main advantage of this Si-interposer is
that it can provide the high alignment
accuracy needed for multi-channel
optical fiber alignment and assembly. For
all photonics communication circuits,
Figure 6: Proposed FOWLP process flow for PIC embedding.
the optical signal of the PIC must be
to 100GHz. The simulated results show the photonics I/O so that a buffer area eventually coupled to the optical fiber for
that the FOWLP interconnect has a large is formed. The buffer area is part of external connection. The fiber assembly
bandwidth and is capable of supporting protection for the photonics I/O facet needs to achieve a high alignment
the high-speed digital signal in the OE. during the subsequent molding process. accuracy in the range of less than 2μm
These excellent electrical performances One of the possible processes that or 1μm (some PIC designs can only
are achieved mainly because of the short could be used to achieve the FOWLP is accept less than 1μm of misalignment) to
interconnect design. described here. The steps are similar to achieve good optical coupling efficiency.
FOWLP photonics process. The the RDL-first process developed by IME I n t h is p rop o se d f ib e r-t o -PIC
key challenge of molding the PIC [5] as shown in Figure 6. The additional assembly solution, the Si-interposer
is to prevent contamination on the process step is to form the stop ring serves as a base substrate to support
photonics I/O facets. The PIC is first (dam). The stop ring is formed using the PIC and a fiber block, which holds
singulated or diced at a distance from a polymer or other suitable material the optical fiber array, as shown in
51
Chip Scale Review January • February • 2022 [ChipScaleReview.com] 51