Page 48 - Chip Scale Review_January February_2022-digital
P. 48
data size is smaller than the weight
parameters, the data communication latency
and energy can be reduced. In [7], it has been
shown that for AlexNet, a CNN implemented
using a FeFET-based PIM accelerator, the
multi-chip design leads to lower energy
efficiency and latency as compared to a
single-chip design. In addition, the multi-
chip design provides higher throughput
because of pipelined execution.
In both NMP and PIM accelerator
architectures, the DRAM, logic, and other
dies come from different process nodes
and are connected using 2D (interposer
and package substrate) or 3D (stacking)
leading to heterogeneous integration. As AI
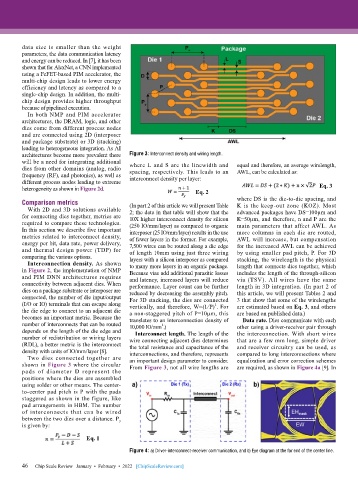
architectures become more prevalent there Figure 3: Interconnect density and wiring length.
will be a need for integrating additional where L and S are the linewidth and equal and therefore, an average wirelength,
dies from other domains (analog, radio spacing, respectively. This leads to an AWL, can be calculated as:
frequency (RF), and photonics), as well as interconnect density per layer:
different process nodes leading to extreme
heterogeneity as shown in Figure 2d. Eq. 3
Eq. 2
where DS is the die-to-die spacing, and
Comparison metrics (In part 2 of this article we will present Table K is the keep-out zone (KOZ). Most
With 2D and 3D solutions available 2; the data in that table will show that the advanced packages have DS=100μm and
for connecting dies together, metrics are 10X higher interconnect density for silicon K=50μm, and therefore, n and P are the
required to compare these technologies. (250 IO/mm/layer) as compared to organic main parameters that affect AWL. As
In this section we describe five important interposer (25 IO/mm/layer) results in the use more columns in each die are routed,
metrics related to interconnect density, of fewer layers in the former. For example, AWL will increase, but compensation
energy per bit, data rate, power delivery, 7,500 wires can be routed along a die edge for the increased AWL can be achieved
and thermal design power (TDP) for of length 10mm using just three wiring by using smaller pad pitch, P. For 3D
comparing the various options. layers with a silicon interposer as compared stacking, the wirelength is the physical
Interconnection density. As shown to many more layers in an organic package. length that connects dies together, which
in Figure 2, the implementation of NMP Because vias add additional parasitic losses includes the length of the through-silicon
and PIM DNN architectures requires and latency, increased layers will reduce via (TSV). All wires have the same
connectivity between adjacent dies. When performance. Layer count can be further length in 3D integration. (In part 2 of
dies on a package substrate or interposer are reduced by decreasing the assembly pitch. this article, we will present Tables 2 and
connected, the number of die input/output For 3D stacking, the dies are connected 3 that show that some of the wirelengths
(I/O or IO) terminals that can escape along vertically, and therefore, W=(1⁄P) . For are estimated based on Eq. 3, and others
2
the die edge to connect to an adjacent die a non-staggered pitch of P=10μm, this are based on published data.)
becomes an important metric. Because the translates to an interconnection density of Data rate. Dies communicate with each
number of interconnects that can be routed 10,000 IO/mm .) other using a driver-receiver pair through
2
depends on the length of the die edge and Interconnect length. The length of the the interconnection. With short wires
number of redistribution or wiring layers wire connecting adjacent dies determines that are a few mm long, simple driver
(RDL), a better metric is the interconnect the total resistance and capacitance of the and receiver circuitry can be used, as
density with units of IO/mm/layer [8]. interconnections, and therefore, represents compared to long interconnections where
Two dies connected together are an important design parameter to consider. equalization and error correction schemes
shown in Figure 3 where the circular From Figure 3, not all wire lengths are are required, as shown in Figure 4a [9]. In
pads of diameter D represent the
positions where the dies are assembled
using solder or other means. The center-
to-center pad pitch is P with the pads
staggered as shown in the figure, like
pad arrangements in HBM. The number
of interconnects that can be wired
between the two dies over a distance. P y
is given by:
Eq. 1
Figure 4: a) Driver-interconnect-receiver communication, and b) Eye diagram at the far end of the center line.
46
46 Chip Scale Review January • February • 2022 [ChipScaleReview.com]