Page 54 - Chip Scale Review_January February_2022-digital
P. 54
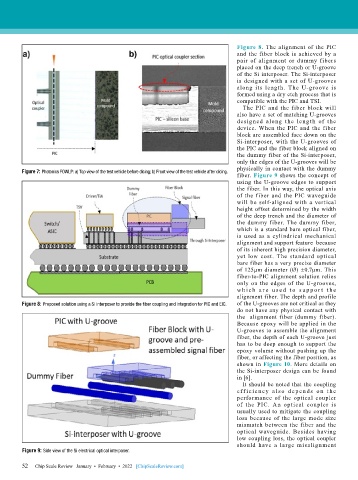
Figure 8. The alignment of the PIC
and the fiber block is achieved by a
pair of alignment or dummy fibers
placed on the deep trench or U-groove
of the Si interposer. The Si-interposer
is designed with a set of U-grooves
along its length. The U-groove is
formed using a dry etch process that is
compatible with the PIC and TSI.
The PIC and the fiber block will
also have a set of matching U-grooves
designed along the length of the
device. When the PIC and the fiber
block are assembled face down on the
Si-interposer, with the U-grooves of
the PIC and the fiber block aligned on
the dummy fiber of the Si-interposer,
only the edges of the U-grooves will be
physically in contact with the dummy
Figure 7: Photonics FOWLP: a) Top view of the test vehicle before dicing; b) Front view of the test vehicle after dicing.
fiber. Figure 9 shows the concept of
using the U-groove edges to support
the fiber. In this way, the optical axis
of the fiber and the PIC waveguide
will be self-aligned with a vertical
height offset determined by the width
of the deep trench and the diameter of
the dummy fiber. The dummy fiber,
which is a standard bare optical fiber,
is used as a cylindrical mechanical
alignment and support feature because
of its inherent high precision diameter,
yet low cost. The standard optical
bare fiber has a very precise diameter
of 125µm diameter (Ø) ±0.7μm. This
fiber-to-PIC alignment solution relies
only on the edges of the U-grooves,
w h i c h a r e u s e d t o s u p p o r t t h e
alignment fiber. The depth and profile
Figure 8: Proposed solution using a Si interposer to provide the fiber coupling and integration for PIC and EIC. of the U-grooves are not critical as they
do not have any physical contact with
the alignment fiber (dummy fiber).
Because epoxy will be applied in the
U-grooves to assemble the alignment
fiber, the depth of each U-groove just
has to be deep enough to support the
epoxy volume without pushing up the
fiber, or affecting the fiber position, as
shown in Figure 10. More details on
the Si-interposer design can be found
in [6].
It should be noted that the coupling
ef f ic ie n c y a l s o d e p e nd s o n t h e
performance of the optical coupler
of the PIC. An optical coupler is
usually used to mitigate the coupling
loss because of the large mode size
mismatch between the fiber and the
optical waveguide. Besides having
low coupling loss, the optical coupler
should have a large misalignment
Figure 9: Side view of the Si electrical optical interposer.
52
52 Chip Scale Review January • February • 2022 [ChipScaleReview.com]