Page 57 - Chip Scale Review_May June_2021-digital
P. 57
Evolution of thermal interface materials for
advanced packaging
By Andy C. Mackie, Ross Berntson [Indium Corporation], Dave Saums [DS&A LLC]
H igh-performance computing
(HPC) is becoming one
of the most impor tant
factors driving growth in advanced
semiconductor manufacturing. The
pandemic of 2020-21 has driven widely-
reported enormous increases in video
data traffic, and with the growth and
ubiquity of Internet of Things (IoT) in
the form of 5G and self-driving cars and
cloud-based artificial intelligence, HPC is
here to stay.
Although there is some debate over the
shrinking logic node designator (7nm,
5nm, 3nm, and so on) as a useful figure
of die performance [1], and, indeed,
whether it still has a physical relevance,
it is interesting to note that the recent
relatively modest improvements in
transistor power consumption (currently
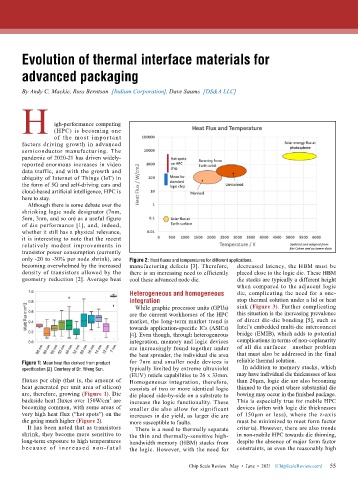
only -20 to -30% per node shrink), are Figure 2: Heat fluxes and temperatures for different applications.
becoming overwhelmed by the increased manufacturing defects [3]. Therefore, decreased latency, the HBM must be
density of transistors allowed by the there is an increasing need to efficiently placed close to the logic die. These HBM
geometry reduction [2]. Average heat cool these advanced node die. die stacks are typically a different height
when compared to the adjacent logic
Heterogeneous and homogeneous die, complicating the need for a one-
integration stop thermal solution under a lid or heat
While graphic processor units (GPUs) sink (Figure 3). Further complicating
are the current workhorses of the HPC this situation is the increasing prevalence
market, the long-term market trend is of direct die-die bonding [5], such as
towards application-specific ICs (ASICs) Intel’s embedded multi-die interconnect
[4]. Even though, through heterogeneous bridge (EMIB), which adds to potential
integration, memory and logic devices complications in terms of non-coplanarity
are increasingly found together under of all die surfaces—another problem
the heat spreader, the individual die area that must also be addressed in the final
Figure 1: Mean heat flux derived from product for 7nm and smaller node devices is reliable thermal solution.
specification [2]. Courtesy of Dr. Yifeng Sun. typically limited by extreme ultraviolet In addition to memory stacks, which
(EUV) reticle capabilities to 26 x 33mm. may have individual die thicknesses of less
fluxes per chip (that is, the amount of Homogeneous integration, therefore, than 20µm, logic die are also becoming
heat generated per unit area of silicon) consists of two or more identical logic thinned to the point where substantial die
are, therefore, growing (Figure 1). Die die placed side-by-side on a substrate to bowing may occur in the finished package.
2
backside heat fluxes over 150W/cm are increase the logic functionality. These This is especially true for mobile HPC
becoming common, with some areas of smaller die also allow for significant devices (often with logic die thicknesses
very high heat flux (“hot spots”) on the increases in die yield, as larger die are of 150µm or less), where the z-axis
die going much higher (Figure 2). more susceptible to faults. must be minimized to meet form factor
It has been noted that as transistors There is a need to thermally separate criteria). However, there are also trends
shrink, they become more sensitive to the thin and thermally-sensitive high- in non-mobile HPC towards die thinning,
long-term exposure to high temperatures bandwidth memory (HBM) stacks from despite the absence of major form factor
b e c au s e of i nc r e a s e d n on -fa t a l the logic. However, with the need for constraints, as even the reasonably high
55
Chip Scale Review May • June • 2021 [ChipScaleReview.com] 55