Page 39 - Chip Scale Review_May June_2021-digital
P. 39
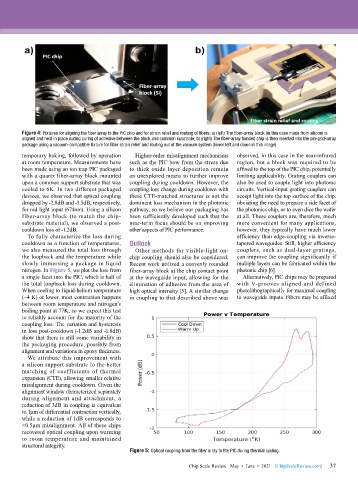
Figure 4: Fixtures for aligning the fiber array to the PIC chip and for strain relief and routing of fibers: a) (left) The fiber-array block (in this case made from silicon) is
aligned and held in place during curing of adhesive between the block and common substrate; b) (right) The fiber-array bonded chip is then inserted into the pin-grid-array
package using a vacuum-compatible fixture for fiber strain relief and routing out of the vacuum system (lower left and down in this image).
temporary baking, followed by operation Higher-order misalignment mechanisms observed, in this case in the near-infrared
at room temperature. Measurements have such as the PIC bow from the stress due region, but a block was required to be
been made using an ion trap PIC packaged to thick oxide layer deposition remain affixed to the top of the PIC chip, potentially
with a quartz fiber-array block mounted an unexplored means to further improve limiting applicability. Grating couplers can
upon a common support substrate that was coupling during cooldown. However, the also be used to couple light into photonic
cooled to 6K. In two different packaged coupling loss change during cooldown with circuits. Vertical-input grating couplers can
devices, we observed that optical coupling these CTE-matched structures is not the accept light into the top surface of the chip,
dropped by -2.8dB and -3.5dB, respectively, dominant loss mechanism in the photonic obviating the need to prepare a side facet of
for red light input (674nm). Using a silicon pathway, so we believe our packaging has the photonics chip, or to even dice the wafer
fiber-array block (to match the chip- been sufficiently developed such that the at all. These couplers are, therefore, much
substrate material), we observed a post- near-term focus should be on improving more convenient for many applications,
cooldown loss of -1.2dB. other aspects of PIC performance. however, they typically have much lower
To fully characterize the loss during efficiency than edge-coupling via inverse-
cooldown as a function of temperatures, Outlook tapered waveguides. Still, higher efficiency
we also measured the total loss through Other methods for visible-light on- couplers, such as dual-layer gratings,
the loopback and the temperature while chip coupling should also be considered. can improve the coupling significantly if
slowly immersing a package in liquid Recent work utilized a convexly rounded multiple layers can be fabricated within the
nitrogen. In Figure 5, we plot the loss from fiber-array block at the chip contact point photonic chip [6].
a single facet into the PIC, which is half of at the waveguide input, allowing for the Alternatively, PIC chips may be prepared
the total loopback loss during cooldown. elimination of adhesive from the area of with V-grooves aligned and defined
When cooling to liquid-helium temperature high optical intensity [5]. A similar change photolithographically for maximal coupling
(~4 K) or lower, most contraction happens in coupling to that described above was to waveguide inputs. Fibers may be affixed
between room temperature and nitrogen’s
boiling point at 77K, so we expect this test
to reliably account for the majority of the
coupling loss. The variation and hysteresis
in loss post-cooldown (-1.2dB and -1.8dB)
show that there is still some variability in
the packaging procedure, possibly from
alignment and variations in epoxy thickness.
We attribute this improvement with
a silicon support substrate to the better
matching of coefficients of thermal
expansion (CTE), allowing smaller relative
misalignment during cooldown. Given the
alignment window characterized separately
during alignment and attachment, a
reduction of 3dB in coupling is equivalent
to 1µm of differential contraction vertically,
while a reduction of 1dB corresponds to
<0.5µm misalignment. All of these chips
recovered optical coupling upon warming
to room temperature and maintained
structural integrity.
Figure 5: Optical coupling from the fiber array to the PIC during thermal cycling.
37
Chip Scale Review May • June • 2021 [ChipScaleReview.com] 37