Page 37 - Chip Scale Review_May June_2021-digital
P. 37
on-chip waveguides, passive components
for mode conversion and beam-splitting,
and diffraction-based grating couplers to
fan out and deliver light to many ions in an
array. For most ion species, several specific
wavelengths of light are required, spanning
the optical spectrum from UV through the
visible to the near infrared. See Figure 1 for
a depiction and realization of this concept.
A particular recent demonstration [4]
enabled delivery of all the optical frequencies
required for control of a Sr+ qubit, a
range extending from 405nm to 1092nm.
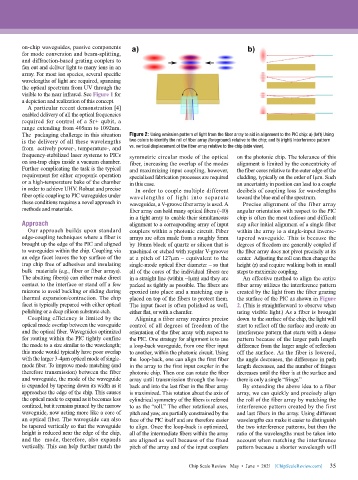
The packaging challenge in this situation Figure 2: Using emission pattern of light from the fiber array to aid in alignment to the PIC chip: a) (left) Using
is the delivery of all these wavelengths two colors to identify the roll of fiber array (foreground) relative to the chip; and b) (right) Interference pattern
from actively power-, temperature-, and vs. vertical displacement of the fiber array relative to the chip (side view).
frequency-stabilized laser systems to PICs symmetric circular mode of the optical on the photonic chip. The tolerance of this
on ion-trap chips inside a vacuum chamber. fiber, increasing the overlap of the modes alignment is limited by the concentricity of
Further complicating the task is the typical and maximizing input coupling, however, the fiber cores relative to the outer edge of the
requirement for either cryogenic operation specialized fabrication processes are required cladding, typically on the order of 1µm. Such
or a high-temperature bake of the chamber in this case. an uncertainty in position can lead to a couple
in order to achieve UHV. Robust and precise In order to couple multiple different decibels of coupling loss for wavelengths
fiber optic coupling to PIC waveguides under wavelengths of light into separate toward the blue end of the spectrum.
these conditions requires a novel approach in waveguides, a V-groove fiber array is used. A Precise alignment of the fiber array
methods and materials. fiber array can hold many optical fibers (~10) angular orientation with respect to the PIC
in a tight array to enable their simultaneous chip is often the most tedious and difficult
Approach alignment to a corresponding array of input step after initial alignment of a single fiber
Our approach builds upon standard couplers within a photonic circuit. Fiber within the array to a single-input inverse-
edge-coupling techniques where a fiber is arrays are often made from a roughly 5mm tapered waveguide. This is because the
brought up the edge of the PIC and aligned by 10mm block of quartz or silicon that is degrees of freedom are generally coupled if
to waveguides within the chip. Coupling via machined or etched with regular V-grooves the fiber array does not pivot precisely at its
an edge facet leaves the top surface of the at a pitch of 127µm – equivalent to the center. Adjusting the roll can then change the
trap chip free of adhesives and insulating single-mode optical fiber diameter – so that height (z) and require walking both in small
bulk materials (e.g., fiber or fiber arrays). all of the cores of the individual fibers are steps to maximize coupling.
The abutting fiber(s) can either make direct in a straight line (within ~1µm) and they are An effective method to align the entire
contact to the interface or stand off a few packed as tightly as possible. The fibers are fiber array utilizes the interference pattern
microns to avoid buckling or sliding during epoxied into place and a matching cap is created by the light from the fiber grazing
thermal expansion/contraction. The chip placed on top of the fibers to protect them. the surface of the PIC as shown in Figure
facet is typically prepared with either optical The input facet is often polished as well, 2. (This is straightforward to observe when
polishing or a deep silicon substrate etch. either flat, or with a chamfer. using visible light.) As a fiber is brought
Coupling efficiency is limited by the Aligning a fiber array requires precise down to the surface of the chip, the light will
optical mode overlap between the waveguide control of all degrees of freedom of the start to reflect off the surface and create an
and the optical fiber. Waveguides optimized orientation of the fiber array with respect to interference pattern that starts with a dense
for routing within the PIC tightly confine the PIC. One strategy for alignment is to use pattern because of the larger path length
the mode to a size similar to the wavelength; a loop-back waveguide, from one fiber input difference from the larger angle of reflection
this mode would typically have poor overlap to another, within the photonic circuit. Using off the surface. As the fiber is lowered,
with the larger 3-4µm optical mode of single- the loop-back, one can align the first fiber the angle decreases, the difference in path
mode fiber. To improve mode matching (and in the array to the first input coupler in the length decreases, and the number of fringes
therefore transmission) between the fiber photonic chip. Then one can rotate the fiber decreases until the fiber is at the surface and
and waveguide, the mode of the waveguide array until transmission through the loop- there is only a single “fringe.”
is expanded by tapering down its width as it back and into the last fiber in the fiber array By extending the above idea to a fiber
approaches the edge of the chip. This causes is maximized. This rotation about the axis of array, we can quickly and precisely align
the optical mode to expand as it becomes less cylindrical symmetry of the fibers is referred the roll of the fiber array by matching the
confined, but it remains pinned by the narrow to as the “roll.” The other rotational axes, interference pattern created by the first
waveguide, now acting more like a core of pitch and yaw, are partially constrained by the and last fibers in the array. Using different
an optical fiber. The waveguide can also face of the PIC itself and are therefore easier wavelengths can make it easier to distinguish
be tapered vertically so that the waveguide to align. Once the loop-back is optimized, the two interference patterns, but then the
height is reduced near the edge of the chip, all of the intermediate fibers within the array ratio of the wavelengths must be taken into
and the mode, therefore, also expands are aligned as well because of the fixed account when matching the interference
vertically. This can help further match the pitch of the array and of the input couplers pattern because a shorter wavelength will
35
Chip Scale Review May • June • 2021 [ChipScaleReview.com] 35