Page 10 - Chip Scale Review_May June_2023-digital
P. 10
MCM rtMLF technology
The following sections discuss various aspects of testing
performed on the MCM rtMLF technology.
Test vehicle and enhancement of small form factor.
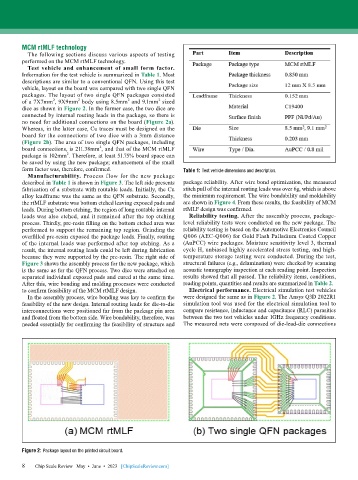
Information for the test vehicle is summarized in Table 1. Most
descriptions are similar to a conventional QFN. Using this test
vehicle, layout on the board was compared with two single QFN
packages. The layout of two single QFN packages consisted
2
2
2
of a 7X7mm , 9X9mm body using 8.5mm and 9.1mm sized
2
dice as shown in Figure 2. In the former case, the two dice are
connected by internal routing leads in the package, so there is
no need for additional connections on the board (Figure 2a).
Whereas, in the latter case, Cu traces must be designed on the
board for the connections of two dice with a 3mm distance
(Figure 2b). The area of two single QFN packages, including
2
board connections, is 211.38mm , and that of the MCM rtMLF
package is 102mm . Therefore, at least 51.75% board space can
2
be saved by using the new package; enhancement of the small
form factor was, therefore, confirmed. Table 1: Test vehicle dimensions and description.
Manufacturability. Process flow for the new package
described in Table 1 is shown in Figure 3. The left side presents package reliability. After wire bond optimization, the measured
fabrication of a substrate with routable leads. Initially, the Cu stitch pull of the internal routing leads was over 6g, which is above
alloy leadframe was the same as the QFN substrate. Secondly, the minimum requirement. The wire bondability and moldability
the rtMLF substrate was bottom etched leaving exposed pads and are shown in Figure 4. From these results, the feasibility of MCM
leads. During bottom etching, the region of long routable internal rtMLF design was confirmed.
leads was also etched, and it remained after the top etching Reliability testing. After the assembly process, package-
process. Thirdly, pre-resin filling on the bottom etched area was level reliability tests were conducted on the new package. The
performed to support the remaining top region. Grinding the reliability testing is based on the Automotive Electronics Council
overfilled pre-resin exposed the package leads. Finally, routing Q006 (AEC-Q006) for Gold Flash Palladium Coated Copper
of the internal leads was performed after top etching. As a (AuPCC) wire packages. Moisture sensitivity level 3, thermal
result, the internal routing leads could be left during fabrication cycle H, unbiased highly accelerated stress testing, and high-
because they were supported by the pre-resin. The right side of temperature storage testing were conducted. During the test,
Figure 3 shows the assembly process for the new package, which structural failures (e.g., delamination) were checked by scanning
is the same as for the QFN process. Two dice were attached on acoustic tomography inspection at each reading point. Inspection
separated individual exposed pads and cured at the same time. results showed that all passed. The reliability items, conditions,
After this, wire bonding and molding processes were conducted reading points, quantities and results are summarized in Table 2.
to confirm feasibility of the MCM rtMLF design. Electrical performance. Electrical simulation test vehicles
In the assembly process, wire bonding was key to confirm the were designed the same as in Figure 2. The Ansys Q3D 2022R1
feasibility of the new design. Internal routing leads for die-to-die simulation tool was used for the electrical simulation tool to
interconnections were positioned far from the package pin area compare resistance, inductance and capacitance (RLC) parasitics
and floated from the bottom side. Wire bondability, therefore, was between the two test vehicles under 1GHz frequency conditions.
needed essentially for confirming the feasibility of structure and The measured nets were composed of die-lead-die connections
Figure 2: Package layout on the printed circuit board.
8 8 Chip Scale Review May • June • 2023 [ChipScaleReview.com]