Page 9 - Chip Scale Review_May June_2023-digital
P. 9
High-performance, multi-chip leadframe package with
internal connections
By DaeYoung Park, HyeongIl Jeon, GiJeong Kim, JiYeon Yang, KwangSoo Sang, ByongJin Kim, JinYoung Khim
[Amkor Technology Korea, Inc.]
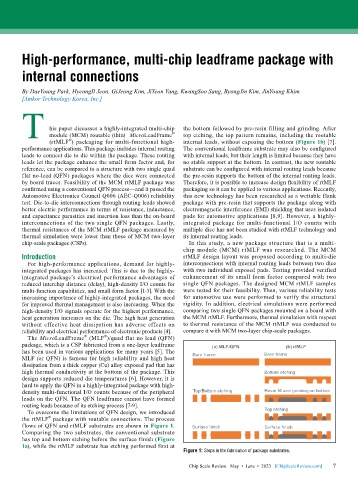
T his paper discusses a highly-integrated multi-chip the bottom followed by pre-resin filling and grinding. After
module (MCM) routable (thin) MicroLeadFrame
®
internal leads, without exposing the bottom (Figure 1b) [7].
(rtMLF ) packaging for multi-functional high- ® top etching, the top pattern remains, including the routable
performance applications. This package includes internal routing The conventional leadframe substrate may also be configured
leads to connect die to die within the package. These routing with internal leads, but their length is limited because they have
leads let the package enhance the small form factor and, for no stable support at the bottom. In contrast, the new routable
reference, can be compared to a structure with two single quad substrate can be configured with internal routing leads because
flat no-lead (QFN) packages where the dice were connected the pre-resin supports the bottom of the internal routing leads.
by board traces. Feasibility of the MCM rtMLF package was Therefore, it is possible to increase design flexibility of rtMLF
confirmed using a conventional QFN process—and it passed the packaging so it can be applied to various applications. Recently,
Automotive Electronics Council Q006 (AEC-Q006) reliability this new technology has been researched as a wettable flank
test. Die-to-die interconnections through routing leads showed package with pre-resin that supports the package along with
better electric performance in terms of resistance, inductance, electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding that uses isolated
and capacitance parasitics and insertion loss than the on-board pads for automotive applications [8,9]. However, a highly-
interconnections of the two single QFN packages. Lastly, integrated package for multi-functional I/O counts with
thermal resistances of the MCM rtMLF package measured by multiple dice has not been studied with rtMLF technology and
thermal simulation were lower than those of MCM two-layer its internal routing leads.
chip-scale packages (CSPs). In this study, a new package structure that is a multi-
chip module (MCM) rtMLF was researched. The MCM
Introduction rtMLF design layout was proposed according to multi-die
For high-performance applications, demand for highly- interconnections with internal routing leads between two dice
integrated packages has increased. This is due to the highly- with two individual exposed pads. Testing provided verified
integrated package’s electrical performance advantages of enhancement of its small form factor compared with two
reduced interchip distance (delay), high-density I/O counts for single QFN packages. The designed MCM rtMLF samples
multi-function capabilities, and small form factor [1-3]. With the were tested for their feasibility. Then, various reliability tests
increasing importance of highly-integrated packages, the need for automotive use were performed to verify the structural
for improved thermal management is also increasing. When the rigidity. In addition, electrical simulations were performed
high-density I/O signals operate for the highest performance, comparing two single QFN packages mounted on a board with
heat generation increases on the die. The high heat generation the MCM rtMLF. Furthermore, thermal simulation with respect
without effective heat dissipation has adverse effects on to thermal resistance of the MCM rtMLF was conducted to
reliability and electrical performance of electronic products [4]. compare it with MCM two-layer chip-scale packages.
®
®
The MicroLeadFrame (MLF )/quad flat no lead (QFN)
package, which is a CSP fabricated from a one-layer leadframe
has been used in various applications for many years [5]. The
MLF (or QFN) is famous for high reliability and high heat
dissipation from a thick copper (Cu) alloy exposed pad that has
high thermal conductivity at the bottom of the package. This
design supports reduced die temperatures [6]. However, it is
hard to apply the QFN in a highly-integrated package with high-
density multi-functional I/O counts because of the peripheral
leads on the QFN. The QFN leadframe cannot have formed
routing leads because of its etching process [7-9].
To overcome the limitations of QFN design, we introduced
®
the rtMLF package with routable connections. The process
flows of QFN and rtMLF substrates are shown in Figure 1.
Comparing the two substrates, the conventional substrate
has top and bottom etching before the surface finish (Figure
1a), while the rtMLF substrate has etching performed first at
Figure 1: Steps in the fabrication of package substrates.
Chip Scale Review May • June • 2023 [ChipScaleReview.com] 7 7