Page 37 - Chip Scale Review_November December_2022-digital
P. 37
ability to scale to finer bond pad pitches, as
further discussed below. This patterning
technology includes the high-speed
measurement of each die location within
a panel, the creation of optimized unit-
specific patterns for each device according
to pre-determined design constraints, and
the application of each layer of the design
file through a maskless lithography system.
Using this patterning technology, simple
devices to complex heterogeneous multi-
chiplet systems can be constructed cost-
effectively with assurance of high yields in
manufacturing.
Multiple techniques are available to
optimize the unit-specific pattern in
response to die shift. The first, adaptive
alignment, typically dynamically aligns the
redistribution layer (RDL) and first via layer
pattern to precisely match that of the die
pads based on the measured lateral shift and
rotation for each die. A further technique,
adaptive routing, builds on top of adaptive
alignment by regenerating small segments
of RDL traces to maintain electrical
connectivity between portions of the design
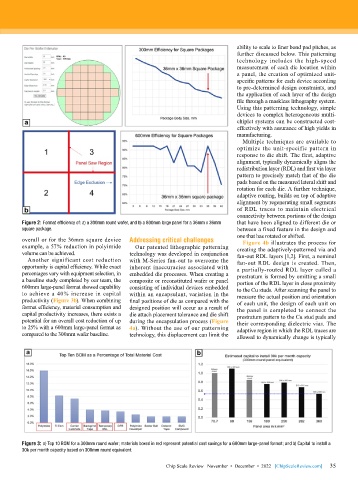
Figure 2: Format efficiency of: a) a 300mm round wafer, and b) a 600mm large panel for a 36mm x 36mm that have been aligned to different die or
square package. between a fixed feature in the design and
one that has rotated or shifted.
overall or for the 36mm square device Addressing critical challenges Figure 4b illustrates the process for
example, a 57% reduction in polyimide Our patented lithographic patterning creating the adaptively-patterned via and
volume can be achieved. technology was developed in conjunction fan-out RDL layers [1,2]. First, a nominal
Another significant cost reduction with M-Series fan-out to overcome the fan-out RDL design is created. Then,
opportunity is capital efficiency. While exact inherent inaccuracies associated with a partially-routed RDL layer called a
percentages vary with equipment selection, in embedded die processes. When creating a prestratum is formed by omitting a small
a baseline study completed by our team, the composite or reconstituted wafer or panel portion of the RDL layer in close proximity
600mm large-panel format showed capability consisting of individual devices embedded to the Cu studs. After scanning the panel to
to achieve a 40% increase in capital within an encapsulant, variation in the measure the actual position and orientation
productivity (Figure 3b). When combining final positions of die as compared with the of each unit, the design of each unit on
format efficiency, material consumption and designed position will occur as a result of the panel is completed to connect the
capital productivity increases, there exists a die attach placement tolerance and die shift prestratum pattern to the Cu stud pads and
potential for an overall cost reduction of up during the encapsulation process (Figure their corresponding dielectric vias. The
to 25% with a 600mm large-panel format as 4a). Without the use of our patterning adaptive region in which the RDL traces are
compared to the 300mm wafer baseline. technology, this displacement can limit the allowed to dynamically change is typically
Figure 3: a) Top 10 BOM for a 300mm round wafer; materials boxed in red represent potential cost savings for a 600mm large-panel format; and b) Capital to install a
30k per month capacity based on 300mm round equivalent.
35
Chip Scale Review November • December • 2022 [ChipScaleReview.com] 35