Page 38 - Chip Scale Review_March April_2022-digital
P. 38
large-size TSV interposers very expensive.
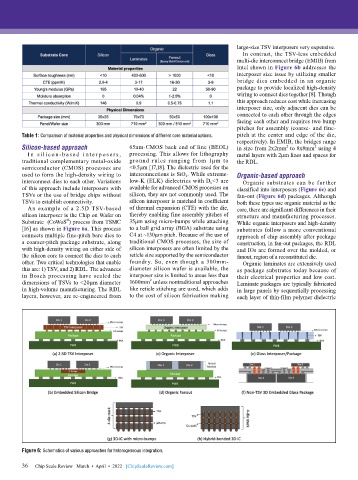
In contrast, the TSV-less embedded
multi-die interconnect bridge (EMIB) from
Intel shown in Figure 6b addresses the
interposer size issue by utilizing smaller
bridge dies embedded in an organic
package to provide localized high-density
wiring to connect dies together [8]. Though
this approach reduces cost while increasing
interposer size, only adjacent dies can be
connected to each other through the edges
facing each other and requires two bump
pitches for assembly (coarse- and fine-
Table 1: Comparison of material properties and physical dimensions of different core material options. pitch at the center and edge of the die,
respectively). In EMIB, the bridges range
Silicon-based approach 65nm-CMOS back end of line (BEOL) in size from 2x2mm to 8x8mm using 4
2
2
I n s i lic o n - b a s e d i n t er p o s er s , processing. This allows for lithography metal layers with 2µm lines and spaces for
traditional complementary metal-oxide ground rules ranging from 1µm to the RDL.
semiconductor (CMOS) processes are <0.5µm [17,18]. The dielectric used for the
used to form the high-density wiring to interconnections is SiO 2 . While extreme- Organic-based approach
interconnect dies to each other. Variations low-K (ELK) dielectrics with D k <3 are Organic substrates can be further
of this approach include interposers with available for advanced CMOS processes on classified into interposers (Figure 6c) and
TSVs or the use of bridge chips without silicon, they are not commonly used. The fan-out (Figure 6d) packages. Although
TSVs to establish connectivity. silicon interposer is matched in coefficient both these types use organic material as the
An example of a 2.5D TSV-based of thermal expansion (CTE) with the die, core, there are significant differences in their
silicon interposer is the Chip on Wafer on thereby enabling fine assembly pitches of structure and manufacturing processes.
Substrate (CoWoS ) process from TSMC 35µm using micro-bumps while attaching While organic interposers and high-density
®
[16] as shown in Figure 6a. This process to a ball grid array (BGA) substrate using substrates follow a more conventional
connects multiple fine-pitch bare dies to C4 at ~130µm pitch. Because of the use of approach of chip assembly after package
a coarser-pitch package substrate, along traditional CMOS processes, the size of construction, in fan-out packages, the RDL
with high-density wiring on either side of silicon interposers are often limited by the and IOs are formed over the molded, or
the silicon core to connect the dies to each reticle size supported by the semiconductor fanout, region of a reconstituted die.
other. Two critical technologies that enable foundry. So, even though a 300mm- Organic laminates are extensively used
this are: 1) TSV, and 2) RDL. The advances diameter silicon wafer is available, the as package substrates today because of
in Bosch processing have scaled the interposer size is limited to areas less than their electrical properties and low cost.
2
dimensions of TSVs to <20µm diameter 1600mm unless nontraditional approaches Laminate packages are typically fabricated
in high-volume manufacturing. The RDL like reticle stitching are used, which adds in large panels by sequentially processing
layers, however, are re-engineered from to the cost of silicon fabrication making each layer of thin-film polymer dielectric
Figure 6: Schematics of various approaches for heterogeneous integration.
36 Chip Scale Review March • April • 2022 [ChipScaleReview.com]
36