Page 62 - ChipScale_Mar-Apr_2021-digital
P. 62
30 minutes of dipping in acetone at higher dielectric reliability will be
room temperature. Another issue was studied, and finally, BHAST analysis
BHAST reliability of the original PID. to demonstrate the improved reliability
The original PID has acid-modified will be reported.
epoxy-acrylate as the main component,
and a residual amount of raw material Design of a new PID
(epichlorohydrin) generated chloride The following sections discuss
ion in the final product. Chloride ion elements of the design of a new PID.
in the acid modified epoxy-acrylate Solvent resistance for fine line
catalyzes the Cu migration and leads to SAP. Generation of microcracks in PID
compromised dielectric reliability. at solvent immersion is explained by
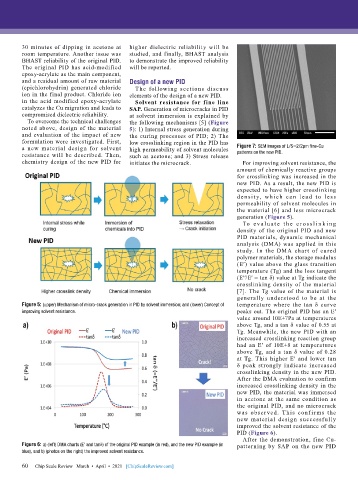
To overcome the technical challenges the following mechanisms [5] (Figure
noted above, design of the material 5): 1) Internal stress generation during
and evaluation of the impact of new the curing processes of PID; 2) The
formulation were investigated. First, low crosslinking region in the PID has
a new material design for solvent high permeability of solvent molecules Figure 7: SEM images of L/S=2/2µm fine-Cu
resistance will be described. Then, such as acetone; and 3) Stress release patterns on the new PID.
chemistry design of the new PID for initiates the microcrack. For improving solvent resistance, the
amount of chemically reactive groups
for crosslinking was increased in the
new PID. As a result, the new PID is
expected to have higher crosslinking
d e n sit y, wh ich c a n le a d t o le s s
permeability of solvent molecules in
the material [6] and less microcrack
generation (Figure 5).
To e v a l u a t e t h e c r o s sl i n k i n g
density of the original PID and new
PID materials, dynamic mechanical
analysis (DMA) was applied in this
study. In the DMA chart of cured
polymer materials, the storage modulus
(E′) value above the glass transition
temperature (Tg) and the loss tangent
(E′′/E′ = tan δ) value at Tg indicate the
crosslinking density of the material
[7]. The Tg value of the material is
generally understood to be at the
Figure 5: (upper) Mechanism of micro-crack generation in PID by solvent immersion; and (lower) Concept of temperature where the tan δ curve
improving solvent resistance. peaks out. The original PID has an E′
value around 10E+7Pa at temperatures
above Tg, and a tan δ value of 0.55 at
Tg. Meanwhile, the new PID with an
increased crosslinking reaction group
had an E′ of 10E+8 at temperatures
above Tg, and a tan δ value of 0.28
at Tg. This higher E′ and lower tan
δ peak strongly indicate increased
crosslinking density in the new PID.
After the DMA evaluation to confirm
increased crosslinking density in the
new PID, the material was immersed
in acetone at the same condition as
the original PID, and no microcrack
was obser ved. This conf ir ms the
new material design successfully
improved the solvent resistance of the
PID (Figure 6).
After the demonstration, fine Cu-
Figure 6: a) (left) DMA charts (E’ and tanδ) of the original PID example (in red), and the new PID example (in patterning by SAP on the new PID
blue), and b) (photos on the right) the improved solvent resistance.
60
60 Chip Scale Review March • April • 2021 [ChipScaleReview.com]