Page 40 - ChipScale_Mar-Apr_2021-digital
P. 40
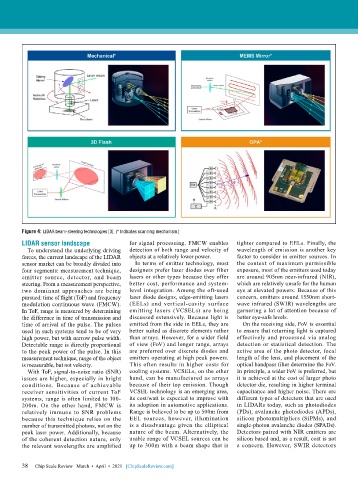
Figure 4: LIDAR beam-steering technologies [3]. (* Indicates scanning mechanism.)
LIDAR sensor landscape for signal processing. FMCW enables tighter compared to EELs. Finally, the
To understand the underlying driving detection of both range and velocity of wavelength of emission is another key
forces, the current landscape of the LIDAR objects at a relatively lower power. factor to consider in emitter sources. In
sensor market can be broadly divided into In terms of emitter technology, most the context of maximum permissible
four segments: measurement technique, designers prefer laser diodes over fiber exposure, most of the emitters used today
emitter source, detector, and beam lasers or other types because they offer are around 905nm near-infrared (NIR),
steering. From a measurement perspective, better cost, performance and system- which are relatively unsafe for the human
two dominant approaches are being level integration. Among the oft-used eye at elevated powers. Because of this
pursued: time of flight (ToF) and frequency laser diode designs, edge-emitting lasers concern, emitters around 1550nm short-
modulation continuous wave (FMCW). (EELs) and vertical-cavity surface wave infrared (SWIR) wavelengths are
In ToF, range is measured by determining emitting lasers (VCSELs) are being garnering a lot of attention because of
the difference in time of transmission and discussed extensively. Because light is better eye-safe levels.
time of arrival of the pulse. The pulses emitted from the side in EELs, they are On the receiving side, FoV is essential
used in such systems tend to be of very better suited as discrete elements rather to ensure that returning light is captured
high power, but with narrow pulse width. than arrays. However, for a wider field effectively and processed via analog
Detectable range is directly proportional of view (FoV) and longer range, arrays detection or statistical detection. The
to the peak power of the pulse. In this are preferred over discrete diodes and active area of the photo detector, focal
measurement technique, range of the object emitters operating at high peak powers. length of the lens, and placement of the
is measurable, but not velocity. This often results in higher costs for optical bandpass filter determine the FoV.
With ToF, signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) cooling systems. VCSELs, on the other In principle, a wider FoV is preferred, but
issues are higher, especially in bright hand, can be manufactured as arrays it is achieved at the cost of larger photo
conditions. Because of achievable because of their top emission. Though detector die, resulting in higher terminal
receiver sensitivities of current ToF VCSEL technology is an emerging area, capacitance and higher noise. There are
systems, range is often limited to 100- its cost/watt is expected to improve with different types of detectors that are used
200m. On the other hand, FMCW is its adoption in automotive applications. in LIDARs today, such as photodiodes
relatively immune to SNR problems Range is believed to be up to 500m from (PDs), avalanche photodiodes (APDs),
because this technique relies on the EEL sources, however, illumination silicon photomultipliers (SiPMs), and
number of transmitted photons, not on the is a disadvantage given the elliptical single-photon avalanche diodes (SPADs).
peak laser power. Additionally, because nature of the beam. Alternatively, the Detectors paired with NIR emitters are
of the coherent detection nature, only usable range of VCSEL sources can be silicon based and, as a result, cost is not
the relevant wavelengths are amplified up to 300m with a beam shape that is a concern. However, SWIR detectors
38 Chip Scale Review March • April • 2021 [ChipScaleReview.com]
38